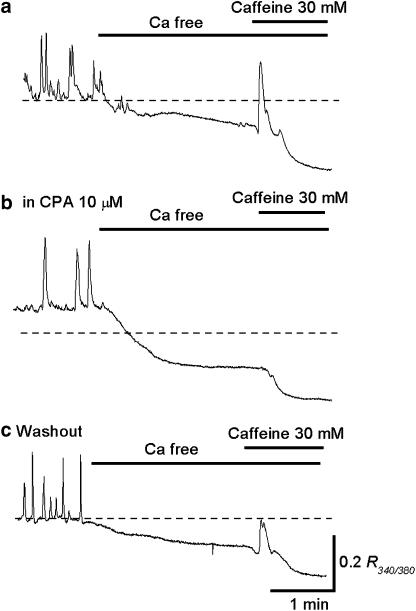
Figure 4.
Effects CPA on caffeine-induced Ca transients in circular smooth muscle of the rabbit urethra. (a) Switching from Krebs' solution to nominally Ca-free solution reduced the basal Ca level and prevented the generation of spontaneous Ca transients. Subsequent caffeine (30 mM) produced a Ca transient and then further reduced the basal Ca level. (b) In the same preparation that had been exposed to CPA (10 μM) for 30 min, caffeine failed to produce Ca transient in nominally Ca-free solution. (c) After washing out CPA, caffeine-induced Ca transients were restored.