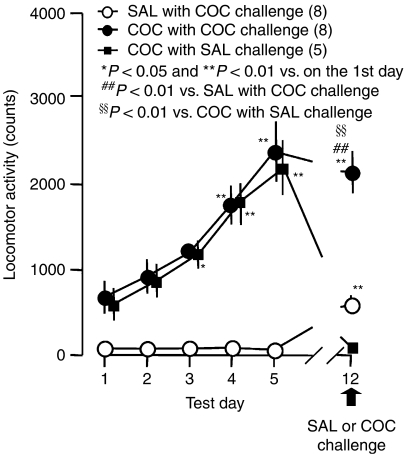
Figure 1.
Repeated administration of cocaine (COC; 10 mg kg−1) induced behavioral sensitization in mice. Twenty-two animals were administered the drug followed by locomotor testing once a day for 5 days. Saline (SAL) with COC challenge was administered to eight mice and COC was administered to14 animals once a day from day 1 to day 5. In mice receiving COC regimen, only one animal did not develop behavioral sensitization and was thus removed from these data but was used in experiments shown in Figure 5 as a nonsensitized animal. Of the remaining 13 mice, those with behavioral sensitization were challenged with cocaine or saline on day 7 of withdrawal: five mice were in the COC with SAL challenge group and eight were in the COC with COC challenge group (10 mg kg−1). The ordinate indicates the total amount of locomotor activity for 3 h after administration. A one-way ANOVA for repeated measures revealed that the significant difference on the test day in SAL with COC challenge (F(5,35)=109.23, P<0.0001), COC with SAL challenge (F(5,20)=42.88, P<0.0001) and COC with COC challenge (F(5,35)=89.83, P<0.0001). *P<0.05 and **P<0.01 vs on test day 1 in each group (Dunnett's test). ##P<0.01 vs SAL with COC challenge and §§P<0.01 vs COC with SAL challenge (F(2,18)=78.75, P<0.0001, a one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's test).