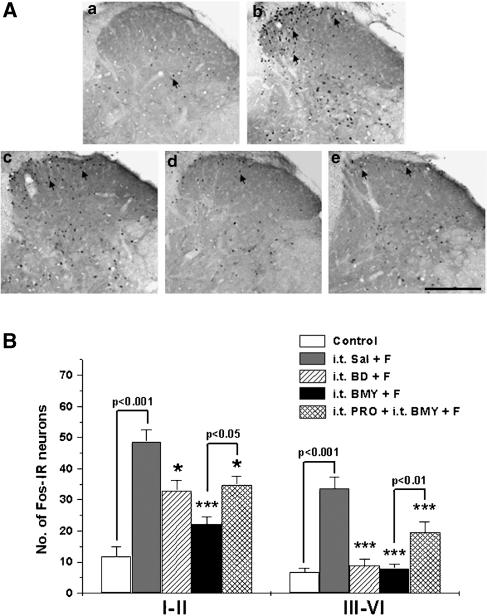
Figure 3.
The suppressive effect of i.t. injection of the spinal σ1 receptor antagonists, BD-1047 (BD) and BMY-14802 (BMY), on formalin (F)-induced spinal Fos expression. Representative spinal cord sections illustrating the typical pattern of Fos expression observed in each of the five groups are shown in the upper panel (A). At 2 h after the formalin injection, the number of Fos immunoreactive (IR) neurons is remarkably increased both in the superficial dorsal horn (laminae I–II) and the intermediate dorsal horn (laminae III–VI) in i.t. saline (Sal)-pretreated mice (spinal cord section ‘b') as compared to control mice (spinal cord section ‘a'). Both i.t. BD-1047 and BMY-14802 significantly suppressed the formalin-induced Fos expression, while i.t. propranolol (PRO) reversed but did not completely abolish the inhibitory effect of BMY-14802 (B). In panel (A), a: control, b: i.t. Sal+F, c: i.t. BD+F, d: i.t. BMY+F, e: i.t. PRO+i.t. BMY+F. Arrows: Fos-IR neurons. Scale bar=200 μm. *P<0.05 and ***P<0.001 as compared with those of i.t. Sal+F group. The number of mice was five in each group.