Fig. 8.
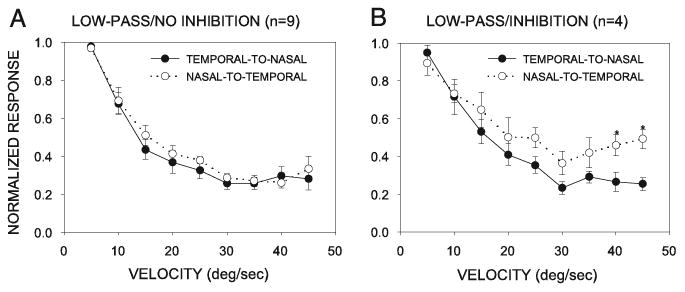
Direction-dependent differences in velocity tuning. Velocity selectivity in the nasal-to-temporal direction of stimulus movement was lower than that in the temporal-to-nasal direction of movement in the LP/I neurons (B), but not DS neurons (A). Data were normalized to the highest response level.
