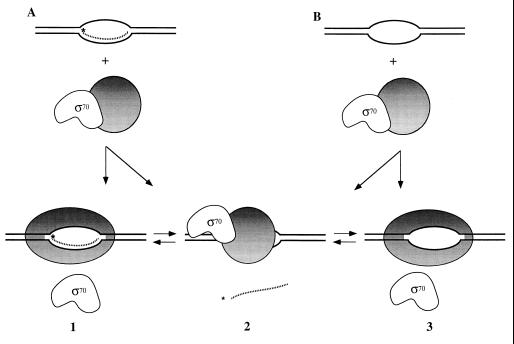
Figure 5.
Release of σ70 or RNA primer on binding of E. coli RNA holopolymerase to DNA bubble-duplex constructs. This schematic depicts the structures proposed for the synthetic elongation complexes present in our assay system. Complexes 1 and 2 are formed on addition of holoenzyme to RNA–DNA bubble duplexes (corresponding to bands I and III of Fig. 4, respectively). Complexes 2 and 3 (the former in the absence of an RNA primer) are formed on addition of holoenzyme to DNA bubble duplexes (corresponding, respectively, to bands III and I of Fig. 4). Core polymerase is depicted as a shaded circle when bound to σ70 and as an ellipse (representing a different conformation) when bound to the DNA bubble. We suggest that this putative conformational change triggers the release of σ70 (complexes 1 and 3). Failure of the polymerase to undergo this conformational change on binding to the bubble-duplex construct induces the release of the RNA strand instead of σ70 (complex 2) and may resemble the events of abortive initiation in promoter-initiated transcription complexes.