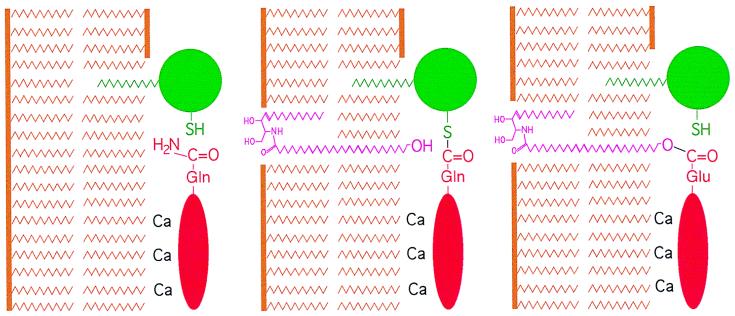
Figure 6.
Model for the reaction of the ω-hydroxyl group of epidermal ceramides. The TGase 1 enzyme (green) and involucrin (red) are bound to cellular membrane bilayers (brown) by acyl lipid adducts and Ca2+ ions, respectively (Left). The catalytic membranes might be either the plasma membrane or the limiting membranes of lamellar bodies (33). The weak nucleophil ω-hydroxyl group is exposed adjacent to the TGase 1-involucrin acyl-enzyme intermediate (Center), resulting in a high likelihood of nucleophilic attack of the thioester bond (Right), resulting in the release of TGase 1 and formation of an ester linkage.