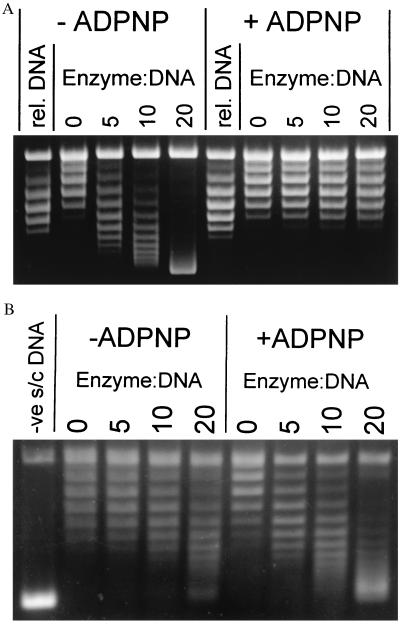
Figure 1.
Topo I relaxation reaction of gyrase–DNA complexes. (A) Typical assay showing the relaxation by topo I of the gyrase-DNA and gyrase–DNA–ADPNP complexes formed on relaxed DNA. The starting material is shown in the track labeled “rel. DNA.” Numbers above the tracks indicate enzyme/DNA ratios; the DNA concentration was 9.4 nM. (Small differences in superhelical density between the starting material and the product of topo I relaxation without gyrase are caused by the different conditions used in the preparation of relaxed DNA.) (B) Trapping of the T segment in the ATP-operated clamp is demonstrated by a similar experiment using A642Phe122B2 and negatively supercoiled DNA. The starting DNA (σ = −0.06) is shown in the track labeled “-ve s/c DNA.” Ciprofloxacin (200 μM) was present in this experiment to stabilize the weak enzyme–DNA complex (14); however, similar results were obtained in the absence of the quinolone. A642Ser122B2 also produced similar results with or without the drug.