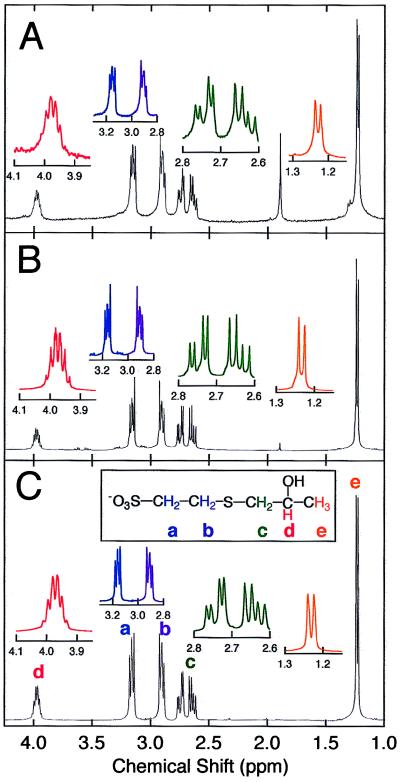
Figure 2.
Spectral identification of epoxypropane-thiol adduct. (A) 1H NMR spectrum of the epoxypropane–cofactor adduct isolated from component I. (B) 1H NMR spectrum of the product of component I-catalyzed reaction of CoM with epoxypropane. (C) 1H NMR spectrum of chemically synthesized 2-hydroxypropyl–CoM. There are five signals (a–e) that correspond to protons on the carbon atoms as indicated in C. The triplet resonances at 2.91 and 3.16 ppm correspond to methylene groups (a) and (b), each integrating to two protons. The protons of methylene group (c) are not chemically equivalent and are therefore split into two quartets with resonances centered at 2.64 and 2.75 ppm, each multiplet integrating to one proton. The sextet at 3.98 ppm corresponds to the proton on carbon (d) and integrates to one proton. The protons of methyl group (e) are split to a doublet at 1.23 ppm that integrates to three protons. The resonance at 1.89 ppm in the isolated epoxypropane–cofactor adduct spectrum (A) is caused by acetate remaining in the sample.