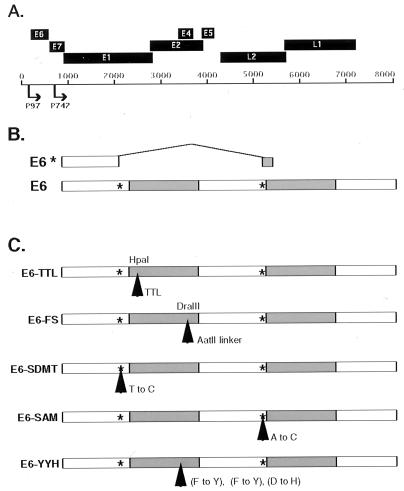
Figure 1.
Schematic of HPV 31 E6 mutants. (A) Diagram representing the ORFs of HPV 31 and the two major promoters that drive viral expression. (B) Diagram depicting the two possible E6 ORFs expressed from the p97-initiated transcripts of HPV 31. E6 represents the full-length protein and E6* denotes a putative shortened protein expressed from a spliced transcript. The asterisks represent the splice-donor and splice-acceptor sites. (C) Diagram showing the HPV 31 E6 mutations with their mutation site(s) indicated by arrows. E6–TTL is an insertion of a TTL, and E6–FS is a frameshift mutant. Both mutants abrogate expression of full-length E6. E6–SDMT and E6–SAM indicate the two splicing mutants with substitutions at nucleotides 212 and 411, respectively, but E6–SDMT and E6–SAM are silent in E6. E6–YYH denotes the p53-binding-deficient mutant with substitutions at amino acids 45, 47, and 49. All mutants were generated in the context of the pBR322.HPV31 construct. Shaded areas represent the zinc finger regions of the protein.