Abstract
Background: The SmD183–119 peptide is a major target of the B cell response in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Objective: To investigate the T cell response directed against this peptide, its disease specificity, and possible impact on SLE pathogenesis.
Methods: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells derived from 28 patients with SLE and 29 healthy and disease controls were stimulated by the SmD183–119 and the recombinant (r)SmD1 protein, and [3H]thymidine incorporation was measured. Patients with SLE were simultaneously tested for autoantibodies, disease activity, clinical symptoms, and medical treatments.
Results: T cell reactivity against the SmD183–119 peptide was detected in 11/28 (39%) patients with SLE and against the rSmD1 protein in 10/28 (36%) patients. In contrast, only 2/29 (7%) controls exhibited SmD1 reactivity. An analysis of proliferation kinetics showed that SmD1 reactive T cells are activated in vivo, as additionally confirmed by cytometric analysis. Addition of mammalian dsDNA to rSmD1 enhanced the rSmD1-specific T cell response. SmD183–119-specific T cell reactivity was significantly more common in patients with cardiac and pulmonary symptoms. No correlation between T and B cell responses and disease activity was seen.
Conclusion: SmD183–119 is a major T cell epitope of SmD1, commonly recognised by T cells from patients with SLE and much less commonly found by healthy or disease controls. This strong T cell reactivity as well as the high frequency and specificity of anti-SmD183–119 antibodies in SLE suggest a possible role in SLE pathogenesis, at least in a subset of patients.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (208.1 KB).
Figure 1 .

Maximal stimulation of PBMC derived from 28 patients with SLE induced by (A) the SmD183–119 peptide and (B) the full length SmD1 protein measured by [3H]thymidine incorporation after three or seven days. Data are shown as median stimulation index (SI), calculated by dividing the mean counts per minute (cpm) of T cell cultures with antigen by the mean cpm of T cell cultures without antigen (medium). All SI≥2 (dashed line) were defined as positive.
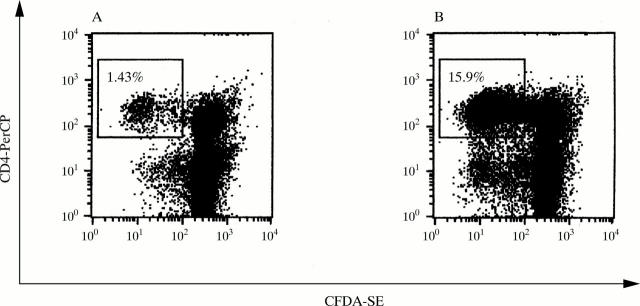
Figure 2 .
Proliferation of CD4 positive T cells derived from a patient with SLE with an SmD183–119-specific T cell reactivity by thymidine assay. PBMC were labelled with CFSE and cultured (A) without or (B) with the SmD183–119 peptide for six days. Sequential halving of CFSE fluorescence intensity is indicative of cell division. Anti-CD4 phenotypic-specific antibodies were used to analyse SmD183–119 specific T helper cells by flow cytometry.
Figure 3 .

Comparison of anti-SmD183–119 and anti-dsDNA autoantibody levels in 32 patients with SLE with the simultaneously analysed T cell reactivity against the SmD183–119 peptide. T cell reactivity was measured by [3H]thymidine incorporation and determined as positive for an SI≥2. Levels of antibodies were detected as arbitrary units (AU) by ELISA. Antibodies were found in both patients with or without a proliferation response of T cells.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angulo R., Fulcher D. A. Measurement of Candida-specific blastogenesis: comparison of carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester labelling of T cells, thymidine incorporation, and CD69 expression. Cytometry. 1998 Jun 15;34(3):143–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bombardier C., Gladman D. D., Urowitz M. B., Caron D., Chang C. H. Derivation of the SLEDAI. A disease activity index for lupus patients. The Committee on Prognosis Studies in SLE. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Jun;35(6):630–640. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher A., Droz D., Adafer E., Noël L. H. Characterization of mononuclear cell subsets in renal cellular interstitial infiltrates. Kidney Int. 1986 May;29(5):1043–1049. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns A., Bläss S., Hausdorf G., Burmester G. R., Hiepe F. Nucleosomes are major T and B cell autoantigens in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Oct;43(10):2307–2315. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200010)43:10<2307::AID-ANR19>3.0.CO;2-J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassese G., Lindenau S., de Boer B., Arce S., Hauser A., Riemekasten G., Berek C., Hiepe F., Krenn V., Radbruch A. Inflamed kidneys of NZB / W mice are a major site for the homeostasis of plasma cells. Eur J Immunol. 2001 Sep;31(9):2726–2732. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(200109)31:9<2726::aid-immu2726>3.0.co;2-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawisha S. M., Gmelig-Meyling F., Steinberg A. D. Assessment of clinical parameters associated with increased frequency of mutant T cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Feb;37(2):270–277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebling F. M., Tsao B. P., Singh R. R., Sercarz E., Hahn B. H. A peptide derived from an autoantibody can stimulate T cells in the (NZB x NZW)F1 mouse model of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Mar;36(3):355–364. doi: 10.1002/art.1780360311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. A., Dyer K., Craven S. Y., Fuller C. R., Yount W. J. Subclass restriction and polyclonality of the systemic lupus erythematosus marker antibody anti-Sm. J Clin Invest. 1985 Apr;75(4):1270–1277. doi: 10.1172/JCI111826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habets W. J., de Rooij D. J., Hoet M. H., van de Putte L. B., van Venrooij W. J. Quantitation of anti-RNP and anti-Sm antibodies in MCTD and SLE patients by immunoblotting. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Feb;59(2):457–466. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn B. H., Singh R. R., Wong W. K., Tsao B. P., Bulpitt K., Ebling F. M. Treatment with a consensus peptide based on amino acid sequences in autoantibodies prevents T cell activation by autoantigens and delays disease onset in murine lupus. Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Feb;44(2):432–441. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200102)44:2<432::AID-ANR62>3.0.CO;2-S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman R. W., Takeda Y., Sharp G. C., Lee D. R., Hill D. L., Kaneoka H., Caldwell C. W. Human T cell clones reactive against U-small nuclear ribonucleoprotein autoantigens from connective tissue disease patients and healthy individuals. J Immunol. 1993 Dec 1;151(11):6460–6469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Vingsbo C., Malmström V., Jansson L., Holmdahl M. Chronicity of arthritis induced with homologous type II collagen (CII) in rats is associated with anti-CII B-cell activation. J Autoimmun. 1994 Dec;7(6):739–752. doi: 10.1006/jaut.1994.1058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holyst M. M., Hill D. L., Hoch S. O., Hoffman R. W. Analysis of human T cell and B cell responses against U small nuclear ribonucleoprotein 70-kd, B, and D polypeptides among patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and mixed connective tissue disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1997 Aug;40(8):1493–1503. doi: 10.1002/art.1780400818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., Mimori T., Takeda Y., Akama H., Yoshida T., Ogasawara T., Akizuki M. Autoantibodies to the Sm antigen: immunological approach to clinical aspects of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1987 Jun;14 (Suppl 13):188–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Incaprera M., Rindi L., Bazzichi A., Garzelli C. Potential role of the Epstein-Barr virus in systemic lupus erythematosus autoimmunity. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1998 May-Jun;16(3):289–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeruc J., Jurcić V., Vizjak A., Hvala A., Babic N., Kveder R., Praprotnik S., Ferluga D. Tubulo-interstitial involvement in lupus nephritis with emphasis on pathogenesis. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2000 Aug 25;112(15-16):702–706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaliyaperumal A., Mohan C., Wu W., Datta S. K. Nucleosomal peptide epitopes for nephritis-inducing T helper cells of murine lupus. J Exp Med. 1996 Jun 1;183(6):2459–2469. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.6.2459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu L., Kaliyaperumal A., Boumpas D. T., Datta S. K. Major peptide autoepitopes for nucleosome-specific T cells of human lupus. J Clin Invest. 1999 Aug;104(3):345–355. doi: 10.1172/JCI6801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons A. B., Parish C. R. Determination of lymphocyte division by flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods. 1994 May 2;171(1):131–137. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(94)90236-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddison P. J., Reichlin M. Quantitation of precipitating antibodies to certain soluble nuclear antigens in SLE. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Apr;20(3):819–824. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mamula M. J., Fatenejad S., Craft J. B cells process and present lupus autoantigens that initiate autoimmune T cell responses. J Immunol. 1994 Feb 1;152(3):1453–1461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohan C., Adams S., Stanik V., Datta S. K. Nucleosome: a major immunogen for pathogenic autoantibody-inducing T cells of lupus. J Exp Med. 1993 May 1;177(5):1367–1381. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.5.1367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monneaux F., Muller S. Laboratory protocols for the identification of Th cell epitopes on self-antigens in mice with systemic autoimmune diseases. J Immunol Methods. 2000 Oct 20;244(1-2):195–204. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(00)00256-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen M. L., Arnett F. C., Reveille J. D. Contrasting molecular patterns of MHC class II alleles associated with the anti-Sm and anti-RNP precipitin autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Jan;36(1):94–104. doi: 10.1002/art.1780360117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou Y., Sun D., Sharp G. C., Hoch S. O. Screening of SLE sera using purified recombinant Sm-D1 protein from a baculovirus expression system. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1997 Jun;83(3):310–317. doi: 10.1006/clin.1997.4355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki S., Berzofsky J. A. Antibody conjugates mimic specific B cell presentation of antigen: relationship between T and B cell specificity. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4133–4142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelfrey C. M., Rudick R. A., Cotleur A. C., Lee J. C., Tary-Lehmann M., Lehmann P. V. Quantification of self-recognition in multiple sclerosis by single-cell analysis of cytokine production. J Immunol. 2000 Aug 1;165(3):1641–1651. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.3.1641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riemekasten G., Kawald A., Weiss C., Meine A., Marell J., Klein R., Hocher B., Meisel C., Hausdorf G., Manz R. Strong acceleration of murine lupus by injection of the SmD1(83-119) peptide. Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Oct;44(10):2435–2445. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200110)44:10<2435::aid-art408>3.0.co;2-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riemekasten G., Marell J., Trebeljahr G., Klein R., Hausdorf G., Häupl T., Schneider-Mergener J., Burmester G. R., Hiepe F. A novel epitope on the C-terminus of SmD1 is recognized by the majority of sera from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1998 Aug 15;102(4):754–763. doi: 10.1172/JCI2749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh R. R., Kumar V., Ebling F. M., Southwood S., Sette A., Sercarz E. E., Hahn B. H. T cell determinants from autoantibodies to DNA can upregulate autoimmunity in murine systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med. 1995 Jun 1;181(6):2017–2027. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.6.2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M. Antinuclear antibodies: diagnostic markers for autoimmune diseases and probes for cell biology. Adv Immunol. 1989;44:93–151. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60641-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theocharis S., Sfikakis P. P., Lipnick R. N., Klipple G. L., Steinberg A. D., Tsokos G. C. Characterization of in vivo mutated T cell clones from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1995 Feb;74(2):135–142. doi: 10.1006/clin.1995.1020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]