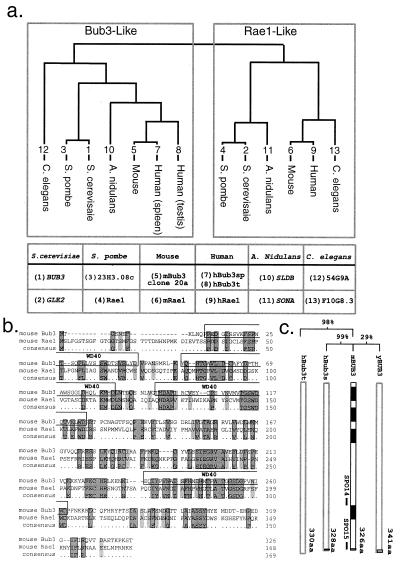
Figure 1.
Sequence analysis of Bub3 and Rae1. (a) A tree generated by phylip (45) comparing sequences listed below and aligned with clustal. Branch lengths are arbitrary, but the connectivity was robust. Bub3 and Rae1 genes from different organisms were obtained as follows: 1) Sc-Bub3, accession number M64707 (17); 2) Sc-Gle2, U18839 (20), 3) Sp-23H3.08c, Z99163; 4) Sp-Rae1, U14951 (21); 5) m-Bub3 (this work); 6, m-Rae1 (this work and ref. 23); 7) h-Bub3, AF053304 for spleen and 8) AF047473 for testis; 9) h-Rae1, U84720 (23); 10) An-SLDB, AF032988 (43); 11) An-SONA, AF069492 (44); 12) Ce-54G9A, AL032648 (l); 13) Ce-F10G8.3, Z80216. (b) Sequence alignment of mouse Bub3 and Rae1 with boxes around four putative WD40 domains (46). (c) Schematic of yeast, mouse, and two human Bub3 proteins showing percent identity and the positions of the SPO14 and SPO15 peptides. Dark boxes denote WD40 repeats.