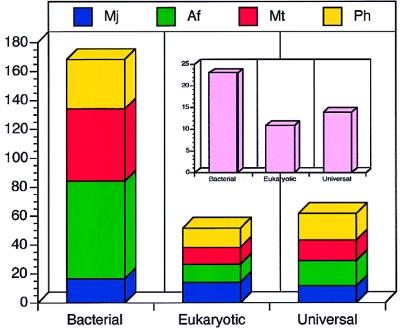
Figure 1.
Distribution of bacterial-, eukaryotic-, and universal transcription-associated homologs in the four complete archaeal genomes of M. jannaschii (blue), A. fulgidus (green), M. thermoautotrophicum (red), and P. horikoshii (yellow). A two-way ANOVA 3 (domain) × 4 (species) (df = 12–1 = 11) for normalized genome compositions (data not shown) of the transcription-associated homologs listed here, suggests that the variance arises mainly from the domain differences (Fd2,11 = 7.76 > F2,11 = 7.21) and not the species differences (Fs3,11 = 0.73 < F3,11 = 6.22) at 99% significance level. The inset represents the distribution of transcription-associated protein families. For ORF identifiers and species distribution of particular families, see Tables 1–3.