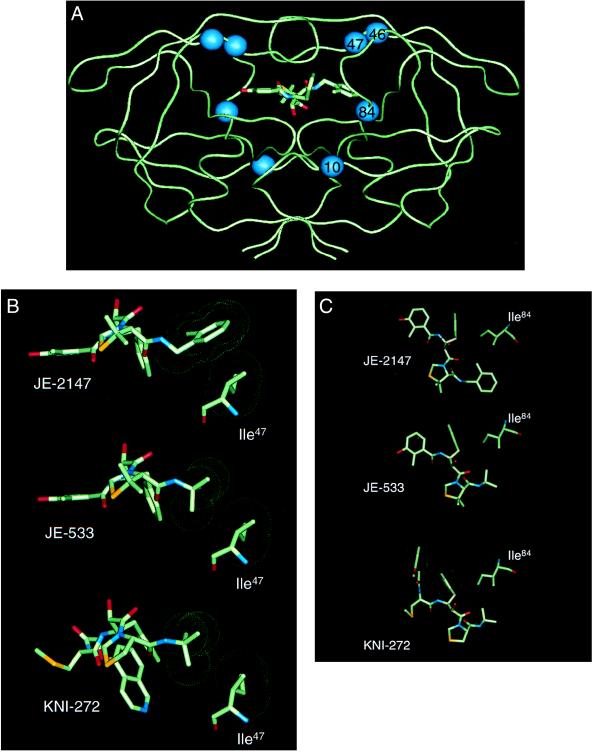
Figure 4.
Crystallographic analysis of enzyme-inhibitor complexes. (A) Backbone representation of the dimeric HIV-1 protease with JE-2147-resistance-associated amino acid substitutions. A model of JE-2147 bound in the active site is shown. Location of residues involved in drug resistance attributable to the in vitro selection with JE-2147 are indicated by spheres. Two of these residues lie within the active site (residues 47 and 84) whereas the other two residues lie outside of the active site (residues 10 and 46). (B) Interactions between Ile47 of wild-type HIV protease and JE-2147, JE-533, or KNI-272. Neither JE-533 or KNI-272 have contacts with Ile47 whereas JE-2147 has a tight interaction with this residue. (C) Interactions between Ile84 of wild-type HIV protease and JE-2147, JE-533, or KNI-272. All three inhibitors make tight interactions with this residue. van der Waals surfaces are shown as dot surfaces; atoms are color-coded by type. The structure of KNI-272 is based on the published crystal structure [Protein Data Bank ID code 1HPX (19)]. The structures of JE-533 and JE-2147 are from unpublished crystal structures (R.K. and J.E., unpublished work).