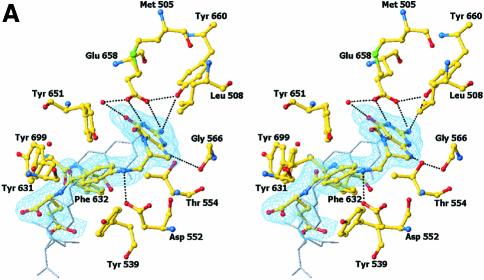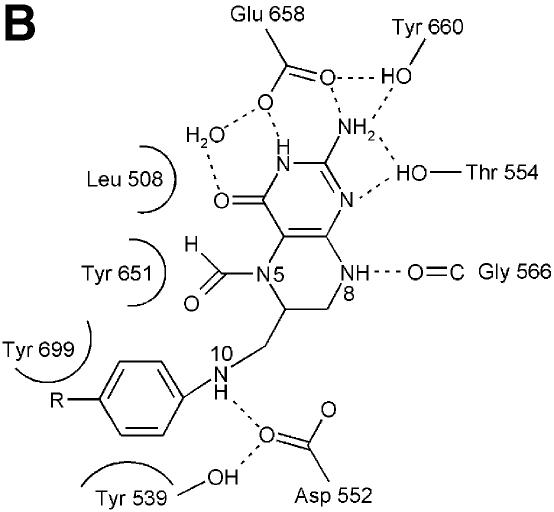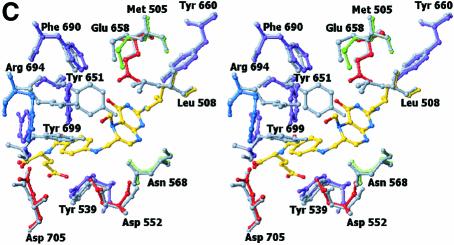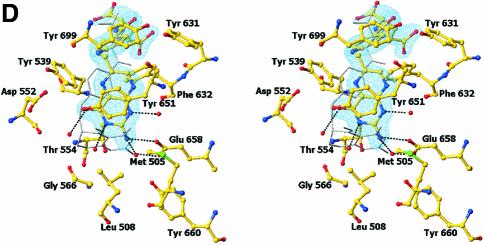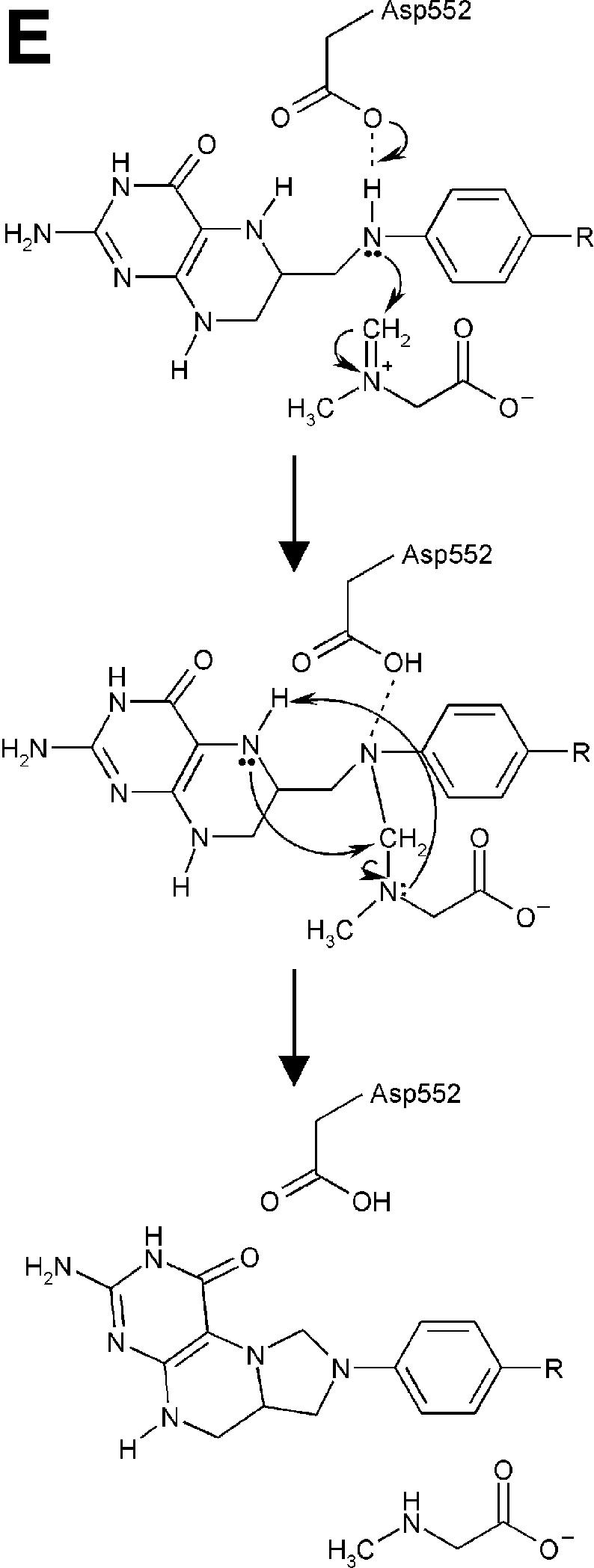
Fig. 4. Structure of the N5,N10-methylene-THF synthase active site. (A) Stereo view of the N5,N10-methylene-THF synthase active site with folinic acid bound. The Fo – Fc omit map is contoured at 3σ around the bound ligand. Residues lining the active site are in ball-and-stick representation coloured according to atom type. Key hydrogen bonds are depicted by black dotted lines. For comparison, the conformation of bound folic acid is represented in thin grey-coloured sticks. (B) Schematic representation of folinic acid bound to DMGO. Hydrogen bonds are indicated by dashed lines. (C) Stereo view of an overlay of the active site in unbound (all atoms grey coloured) and folinic acid-bound conformation (residues coloured according to residue type). (D) Stereo view of the N5,N10-methylene-THF synthase active site with folic acid bound. The Fo – Fc omit map is shown contoured at 3σ around the bound ligand; atoms are coloured according to atom type. Key hydrogen bonds are depicted by black dotted lines; for comparison, the conformation of bound folinic acid is represented in thin grey-coloured sticks. (E) Schematic representation of the N5,N10-methylene-THF synthase reaction. The bound THF attacks the iminium ion via the nucleophilic N10 group with concomitant proton abstraction by Asp552. The next step involves the attack by the N5 group on the covalent intermediate with concomitant deprotonation of the N5 by the nascent sarcosine. An alternative possibility is that the N5 position attacks first and donates a proton to the covalent intermediate, followed by the nucleophilic attack of the N10 group with release of sarcosine.