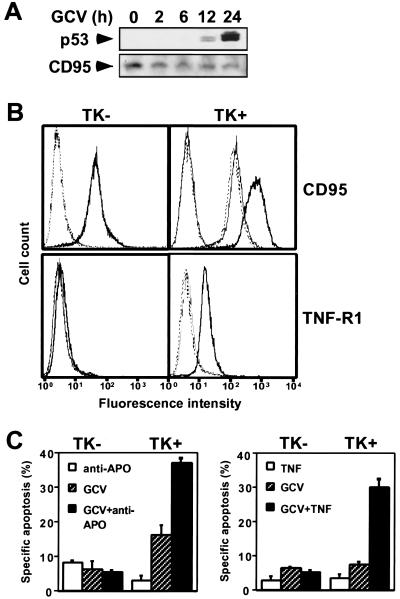
Figure 3.
TK/GCV induces p53, up-regulates death receptors likely involving p53-mediated translocation of CD95, and sensitizes to death-inducing ligands. SH-EP pHyTK11 cells (TK+) were compared with SH-EP pLXSN cells (TK−). (A) TK/GCV induces p53 but not CD95. Cells were treated with 10 μM of GCV for the times indicated. Protein was extracted and separated by SDS/PAGE, and p53 and CD95 were detected by immunoblot. (B) TK/GCV up-regulates death receptors on the cell surface likely involving p53-mediated translocation of CD95. SH-EP pHyTK11 (TK+) and SH-EP pLXSN (TK−) cells were treated with 10 μM of GCV for 24–48 h in the absence or presence of brefeldin A, and expression of CD95 and TNF-R1 was determined by flow cytometry. Bold, solid line, stained cells treated with GCV; thin, solid line, stained cells treated with GCV in the presence of brefeldin A; broken line, stained untreated cells; dotted line, unstained cells. Results are means of triplicates, and similar results were obtained in two separate experiments. (C) TK/GCV sensitizes to death-inducing ligands. Cells (2 × 104) were treated with 10 μM of GCV for 24 h followed by incubation without GCV for an additional 48 h in the presence or absence of either 0.1 μg anti-APO-1 with 5 ng/ml of protein A, 100 ng/ml of TNF, or 1:30 TRAIL. Apoptosis was determined as described in Materials and Methods. Results are means of triplicates, and similar results were obtained in two separate experiments.