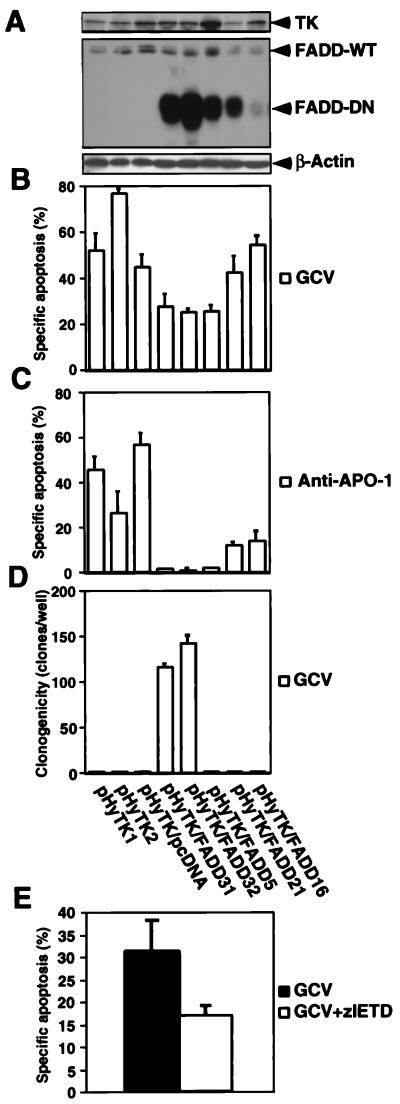
Figure 5.
TK/GCV-mediated apoptosis is attenuated by FADD-DN and inhibition of caspase-8. Clones stably transfected with either TK (pHyTK1 and 2) or with TK and an empty pcDNA3 vector (pHyTK1/pcDNA) were compared with clones stably transfected both with TK and FADD-DN (pHyTK/FADD31, 32, 5, 21, and 16). (A) All clones express TK as well as wild-type FADD. Clones bearing FADD-DN express it to varying degrees. Protein expression was detected by immunoblot by using polyclonal anti-TK and monoclonal anti-FADD antibodies. Equal gel loading was controlled by detection of β-actin. (B) TK/GCV-mediated apoptosis is inhibited by FADD-DN. Cells were treated with 10 μM of GCV for 72 h, and apoptosis was assessed. (C) Anti-APO-1-induced apoptosis is inhibited by FADD-DN depending on the extent of expression of the mutated protein. Cells were treated with 1 μg/ml of anti-APO-1, 5 ng/ml of protein A, and 2 μg/ml of cycloheximide for 12 h, and apoptosis was assessed. (D) TK/GCV decreases clonogenicity depending on FADD function. Cells were treated with 10 μM of GCV for 9 days, and 500 cells were replated in six-well plates. After 4 days of culture, the colony number per well was determined. (E) TK/GCV-induced apoptosis is inhibited by the caspase-8 inhibitor zIETD-fmk. Cells were treated for 48 h with 10 μM of GCV in the absence and presence of 50 μM zIETD-fmk. Medium including GCV and zIETD-fmk was changed after 24 h. Apoptosis was determined as described in Materials and Methods. Results are means of triplicates, and similar results were obtained in two separate experiments.