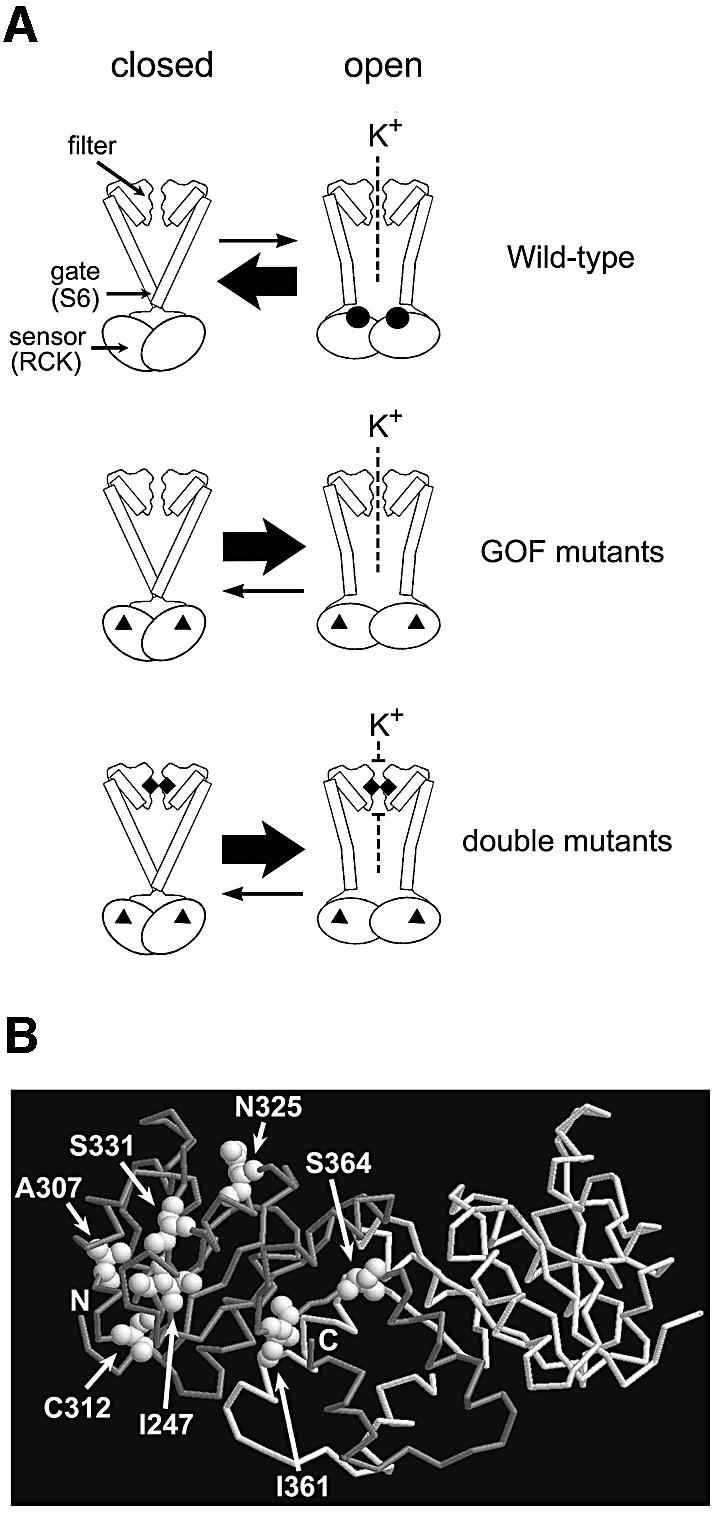
Fig. 8. A model of the functional parts of Kch and the locations of the GOF mutations in RCK. (A) Diagram of the wild-type, the GOF mutant and the double mutant Kch channels. Top: the wild-type Kch only opens briefly when ligands (black circles) bind to its cytoplasmic sensor domain (RCK). Middle: the GOF mutations (black triangles) in the RCK domain bias the sensor towards its open configuration even without the ligand. Bottom: a mutation (black diamonds) in the K+ filter disrupts the filter and blocks the K+ permeation. (B) A map of the GOF mutations in the RCK dimer of Kch (Jiang et al., 2001; PDB code 1ID1). I247, A307 and C312 are toward the core of the Rossmann fold. N325 and S331 are on the hydrophobic interface. I361 and S364 are at the hinge/flexible interface.
