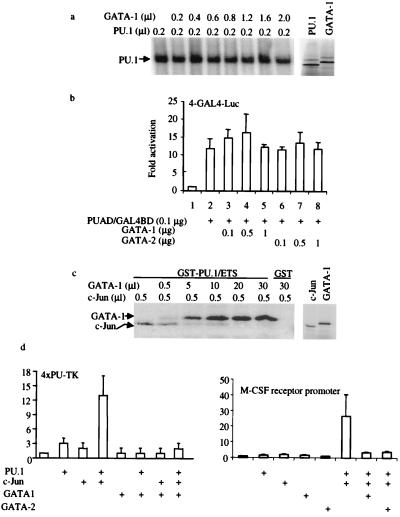
Figure 4.
GATA proteins inhibit PU.1 transactivation by displacing the PU.1 coactivator, c-Jun. (a) GATA proteins do not inhibit PU.1 binding to DNA. (Left) EMSA using a α-32P-ATP-labeled PU.1-binding-site probe (32) and in vitro transcribed and translated PU.1 and GATA-1 proteins. PU.1 protein (0.2 μl) was used for each reaction, along with increasing amounts of GATA-1 protein as indicated. (Right) SDS/PAGE gel of in vitro transcribed and translated 2 μl of PU.1 and 2 μl of GATA used in EMSA. (b) GATA-1 and GATA-2 do not inhibit PU.1 activation domain function. CV-1 cells were transfected with 4 μg of multimerized GAL4 DNA-binding sites in front of a minimal TK promoter used as a reporter. One hundred nanograms of PU.1 activation domain/GAL4 DNA-binding domain fusion protein (PUAD/GAL4BD) in pcDNA3 was used as a transactivator, and GATA-1 or GATA-2 was added as indicated. Luciferase activities were corrected by an internal-control Renilla luciferase vector and shown as fold activation (±SD; n = 3). (c) GATA-1 inhibits c-Jun binding to PU.1. (Left) In vitro 35S-methionine-labeled c-Jun or GATA-1 was incubated with GST-PU.1 Ets domain (GST-PU.1/ETS) or GST alone (GST). The amounts of GATA-1 and c-Jun added are indicated at the top. (Right) SDS/PAGE gel of c-Jun (1 μl) and GATA-1 (2 μl) used in the GST pull-down experiment. (d) GATA-1 inhibits c-Jun coactivation of PU.1 function. F9 cells were transfected by using Lipofectamine Plus with 0.3 μg of 4XPU-TK, 0.1 μg of PU.PECE, 0.05 μg of pSV-Sport1-c-Jun [a c-Jun expression vector (20)], and 1.3 μg of pcDNA3-GATA-1. Luciferase activates were determined 24 hr after transfection and shown as fold activation (±SD; n = 3). The same experiments were done by using the M-CSF receptor promoter-luciferase reporter as shown (Right) using GATA-1 or GATA-2.