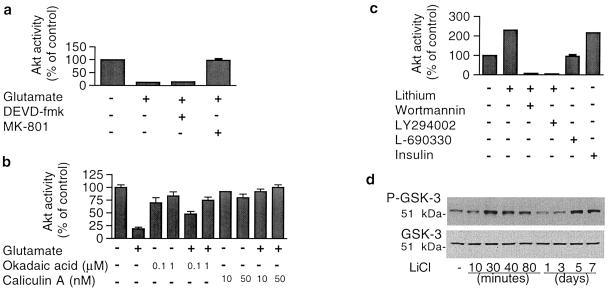
Figure 4.
Pharmacological and biochemical characterization of glutamate-decreased and lithium–increased Akt-1 activity. (a) MK-801, an NMDA receptor antagonist, prevented glutamate-induced inhibition of Akt-1 activity, whereas the fluoromethyl ketone peptide analog Z-DEVD-fmk, a caspase 3 inhibitor, did not. Cells at day 8 in vitro were treated with 10 μM MK-801 or 200 μM Z-DEVD-fmk for 40 min and then treated with 50 μM glutamate for 30 min for the Akt-1 kinase activity assay. (b) Effects of protein phosphatase inhibitors on glutamate-inhibited Akt-1 activity: Cells were pretreated with the indicated concentrations of okadaic acid or caliculin A for 60 min before exposure to 50 μM glutamate for 15 min and assayed for Akt-1 kinase activity. (c) Characterization of lithium-induced Akt-1 activation: Cells at day 8 in vitro were treated with 3 mM LiCl for 20 min without or with 30-min pretreatment with 100 nM wortmannin or 10 μM LY294002. When indicated, cells were also treated with 200 μM L-690330 (an inositol monophosphatase inhibitor) or 2 μM insulin for 20 min and assayed for Akt-1 activity. (d) Time-course of effects of lithium on GSK-3 α (Ser21) phosphorylation and total GSK-3: CGCs were treated with 3 mM LiCl for indicated times and immunoblotting was performed with phospho-specific (Ser21) antibody to GSK-3 α (Upper blot) and total GSK-3 antibody (Lower blot). Representative immunoblots from two experiments are shown. Quantified results in a, b, and c are means ± SEM from at least four independent experiments.