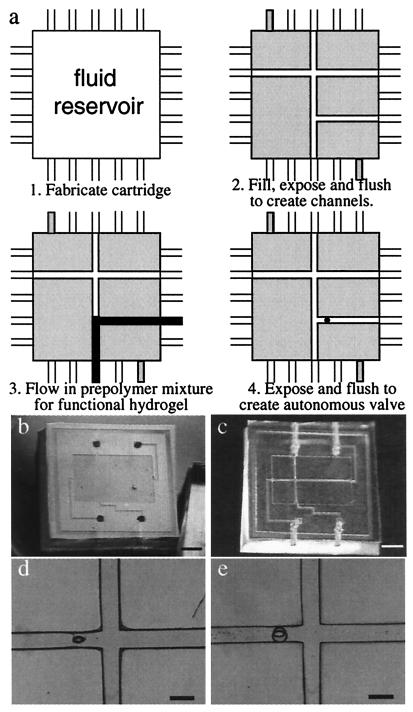
Figure 4.
System construction using μFT. (a) A schematic of the steps to fabricate a functional microfluidic system using μFT. (b) The PDMS/glass tectonics cartridge. PDMS substrate with a shallow and wide fluidic chamber (i.e., Tectonics cartridge; 12-mm ×18-mm wide, 200-μm deep) was molded in a Petri dish by using a positive relief master. The inlet/outlet connection channels were cored through the side of the block to retain complete optical access over the entire cartridge. A microscope cover glass was bonded to the PDMS substrate as the cartridge top after activating the surface with oxygen plasma in an reactive ion etch system. (c and d) The tectonics cartridge after simultaneous fabrication of a microchannel and a post using a multipattern photomask. The prepolymer mixture for this construction material consists of IBA and TeEGDMA (in a 9:1 weight ratio) and Irgacure 651 (3.0 wt %). The UV source is a 200-W mercury lamp (≈400 mJ/cm2), and the exposure time is 1 min. (e) The pH-sensitive hydrogel jacket around the post after exposure and flushing. The prepolymer mixture for this pH-sensitive hydrogel consists of acrylic acid and 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) (in a 1:4 molar ratio), ethyleneglycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA, 1.0 wt %), and Irgacure 651 (3.0 wt %). [Bars = 5,000 μm (b and c) and 500 μm (d and e).]