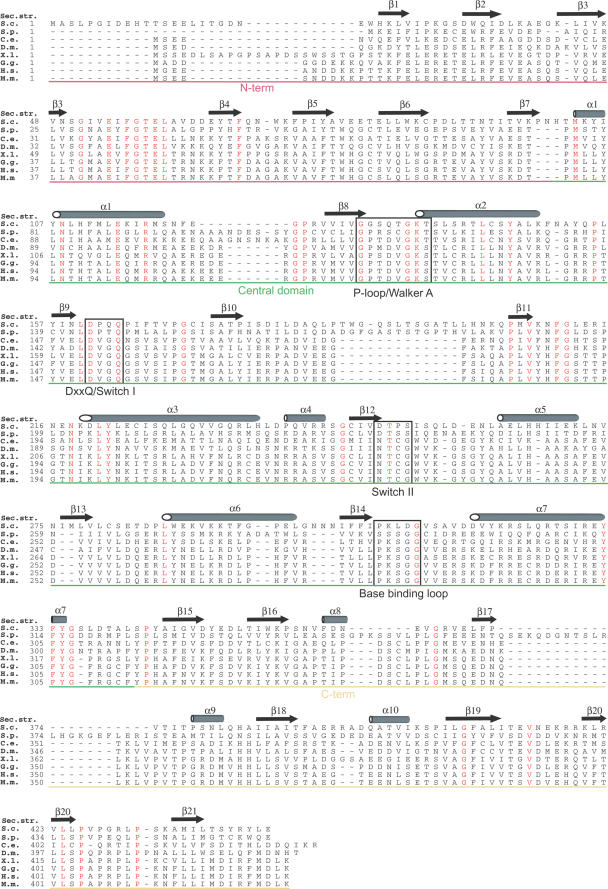
Figure 3.
Clp1 sequence alignment. A sequence alignment of Clp1 proteins from across the eukaryotic kingdom. S. c. S.cerevisiae (swissprot accession no., Q08685), S. p. Schizosaccharomyces pombe (swissprot accession no., Q10299), C. e. Caenorhabditis elegans (swissprot accession no., P52874), D. m. Drosophila melanogaster (swissprot accession no., Q9V6Q1), X. l. Xenopus laevis (swissprot accession no., Q6NS21), G. g. Gallus gallus (swissprot accession no., Q5ZJL4), H. s. Homo sapiens (swissprot accession no., Q92989), M. m. Mus musculus (swissprot accession no., Q99LI9). The position of secondary structure elements observed in the S.cerevisiae Clp1 structure are shown above the alignment, residues that are identical in all species are highlighted in red and sequence motifs involved in ATP-binding and catalysis are boxed. The regions corresponding to each domain, coloured as in Figure 2, are indicated.