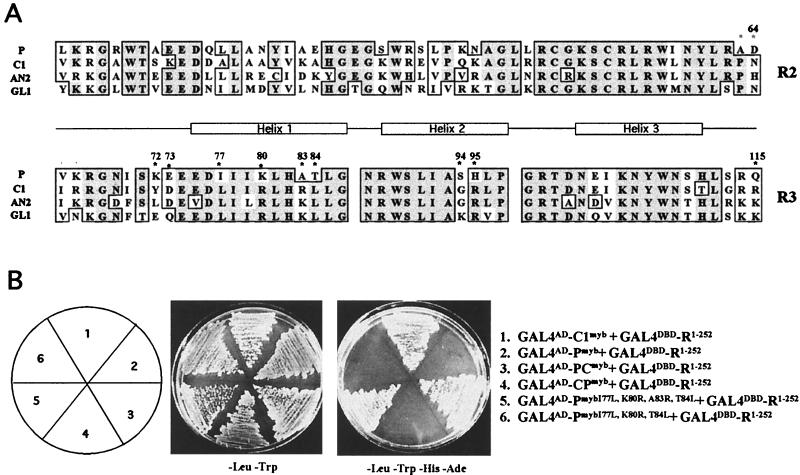
Figure 2.
Myb domain sequences that contribute to the specificity of the interaction with the bHLH cofactor R. (A) Sequence comparison between the Myb domains of P (25), and other proteins shown to interact with R, including C1 (37), AN2 (32), and GL1 (38). The position of the three α-helices that form each Myb repeat are marked, with helix 3 of each motif involved in DNA interaction. Residue numbers are based on the sequences of P and C1. Dark shading indicates identical residues, light shading indicates conservative changes. Residues focused on in this study are marked with asterisks. (B) Yeast two-hybrid interactions of the Myb domains of C1, P, or mutant versions of the Myb domain of P fused to the Gal4 activation domain (GAL4AD) with the N-terminal 252 amino acids of R fused to the GAL4 DNA-binding domain (GALDBD). The simultaneous change of the I77, K80, A83, and T84 residues in P for the corresponding residues of C1 (Gal4AD-PmybI77L,K80R,A83R,T84L) allow P to interact with R.