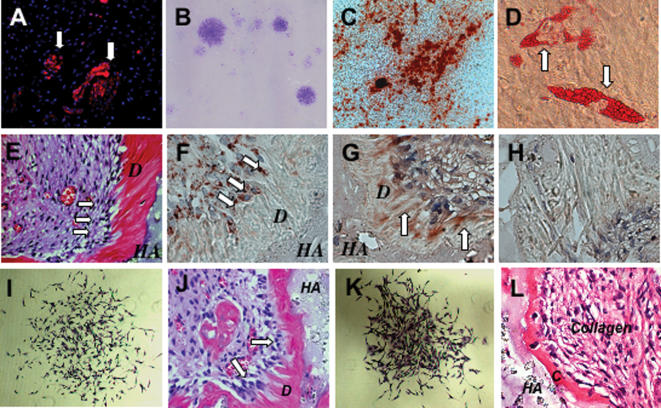
Figure 1. Isolation of Stem Cells from Root Apical Papilla (SCAP).
(A) Human apical papilla tissue was positive for STRO-1, an early mesenchymal progenitor marker, staining by immunofluorescence (arrows).
(B) Single colonies were formed after human SCAP were plated at a low density (5×103/T25 flask) and cultured for 10 days.
(C) When human SCAP were cultured in odontogenic/osteogenic inductive conditions containing L-ascorbate-2-phosphate, dexamethasone, and inorganic phosphate for 4 weeks, mineralized nodules were found by Alizarin red S staining.
(D) Cultured human SCAP formed Oil red O positive lipid clusters following 5 weeks of adipogenic induction in the presence of 0.5 mM isobutylmethylxanthine, 0.5 µM hydrocortisone, 60 µM indomethacin, and 10 µg/ml insulin.
(E) Eight weeks after transplantation in immunocompromised mice, human SCAP differentiated into odontoblasts (arrows) that formed dentin (D) on the surfaces of a hydroxyapatite tricalcium (HA) carrier.
(F) Immunohistochemical staining showed that human SCAP differentiated into odontoblasts (arrows) that were positive for anti-human specific mitochondria antibody staining.
(G) Immunohistochemical staining showed that human SCAP-generated dentin (D) was positive for anti-DSP antibody staining (arrows).
(H) Pre-immunoserum negative control of human SCAP transplant.
(I) SCAP isolated from swine were capable of forming a single colony cluster when plated at a low cell density.
(J) When transplanted into immunocompromised mice for 8 weeks, swine SCAP differentiate into odontoblasts (arrows) to regenerate dentin (D) on the surface of the hydroxyapatite carrier (HA).
(K) Swine PDLSCs were capable of forming a single colony cluster.
(L) After transplantation into immunocompromised mice, swine PDLSCs formed cementum (C) on the surface of hydroxyapatite carrier (HA).
Collagen fibers were found to connect to newly formed cementum.