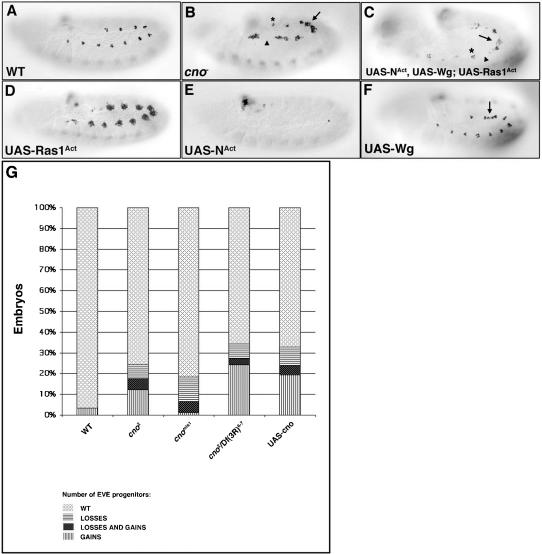
Figure 2.
cno2 zygotic null mutants display gain and loss of progenitors.
All panels show lateral views of stage 11 embryos stained with an α-Eve antibody.
(A) Eve wildtype (wt) expression in a subset of dorsal muscle/heart progenitors and founder cells (2–3 cells) per hemisegment.
(B) cno2 mutants show gain (arrow), loss (arrowhead) or a wildtype number (asterisk) of Eve+ progenitors in different hemisegments.
(C) Embryos in which NAct, Wg and RasAct are simultaneously expressed in the mesoderm display a cno2-like phenotype: gain (arrow), loss (arrowhead) and wildtype number of Eve+ progenitors (asterisk).
(D) Overexpression of Ras1Act in the mesoderm induces the specification of extra Eve+ progenitors.
(E) Overexpression of NAct in the mesoderm inhibits Eve+ progenitor specification.
(F) Embryos in which Wg is overexpressed in the mesoderm show gain of Eve+ progenitors in intersegmental regions (arrow).
(G) Table shows % of embryos of the indicated genotype that display a wildtype number of Eve+ progenitors, Eve+ progenitors gain, loss and both (gain and loss).
cno2 and cnomis1 are null and hypomorph mutant alleles, respectively; Df(3R)6-7 removes cno. cno gof phenotype (UAS-cno) is also variable.
Legends for bars are shown below the table.
At least 70 embryos of each genotype were counted. P<0.0001 for all genotypes except for cnomis1 (P = 0.0017).