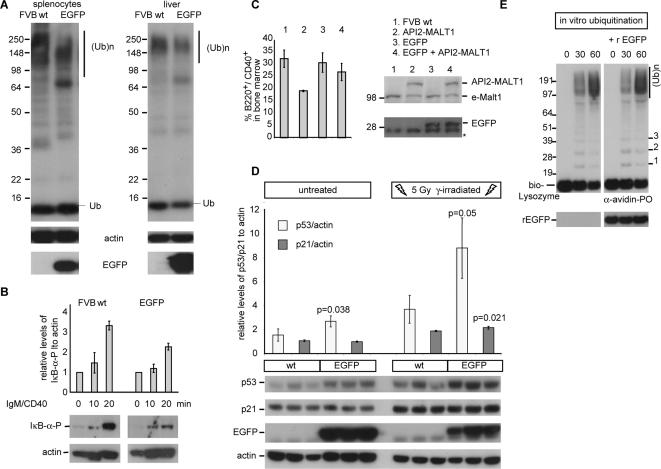
Figure 3. EGFP affects polyubiquitination-dependent processes in vivo.
(A) Western blots of spleen and liver extracts from FVB wild-type (wt) and EGFP transgenic mice detected with antibodies against Ubiquitin, EGFP and actin (loading control).
(B) EGFP reduces phosphorylation of IκB-α in anti-IgM/anti-CD40 stimulated B-lymphocytes purified from EGFP mice.
Experiments performed in triplicate, a representative image of one experiment is shown.
The average and standard deviations of ratios of IκB-α-P to actin relative to un-stimulated cells are given.
(C) The deficit of B220+/CD40+ B-cells in the bone marrow of API2-MALT1 mice is restored in EGFP/API2-MALT1 double transgenic mice.
Experiments performed in triplicate, the average and standard deviations are depicted. eMalt1: endogenous Malt1, *a-specific band (D) EGFP mice show increased p53 levels in the liver and have enhanced p53/p21 responses upon γ-irradiation induced DNA damage.
The average and standard deviations of the ratios of p53/p21 to actin signals relative to that of sample 1 are given.
(E) Recombinant EGFP (rEGFP) does not prevent polyubiquitination of a Biotin-Lysozyme substrate in vitro. (Ub)n: polyubiquitinated proteins.