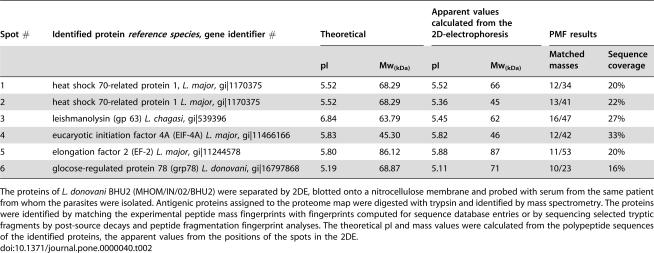
Table 2. Antigens in human visceral leishmaniasis identified by proteome serology.
| Spot # | Identified protein reference species, gene identifier # | Theoretical | Apparent values calculated from the 2D-electrophoresis | PMF results | |||
| pI | Mw(kDa) | pI | Mw(kDa) | Matched masses | Sequence coverage | ||
| 1 | heat shock 70-related protein 1, L. major, gi|1170375 | 5.52 | 68.29 | 5.52 | 66 | 12/34 | 20% |
| 2 | heat shock 70-related protein 1 L. major, gi|1170375 | 5.52 | 68.29 | 5.36 | 45 | 13/41 | 22% |
| 3 | leishmanolysin (gp 63) L. chagasi, gi|539396 | 6.84 | 63.79 | 5.45 | 62 | 16/47 | 27% |
| 4 | eucaryotic initiation factor 4A (EIF-4A) L. major, gi|11466166 | 5.83 | 45.30 | 5.82 | 46 | 12/42 | 33% |
| 5 | elongation factor 2 (EF-2) L. major, gi|11244578 | 5.80 | 86.12 | 5.88 | 87 | 11/53 | 20% |
| 6 | glocose-regulated protein 78 (grp78) L. donovani, gi|16797868 | 5.19 | 68.87 | 5.11 | 71 | 10/23 | 16% |
The proteins of L. donovani BHU2 (MHOM/IN/02/BHU2) were separated by 2DE, blotted onto a nitrocellulose membrane and probed with serum from the same patient from whom the parasites were isolated. Antigenic proteins assigned to the proteome map were digested with trypsin and identified by mass spectrometry. The proteins were identified by matching the experimental peptide mass fingerprints with fingerprints computed for sequence database entries or by sequencing selected tryptic fragments by post-source decays and peptide fragmentation fingerprint analyses. The theoretical pI and mass values were calculated from the polypeptide sequences of the identified proteins, the apparent values from the positions of the spots in the 2DE.