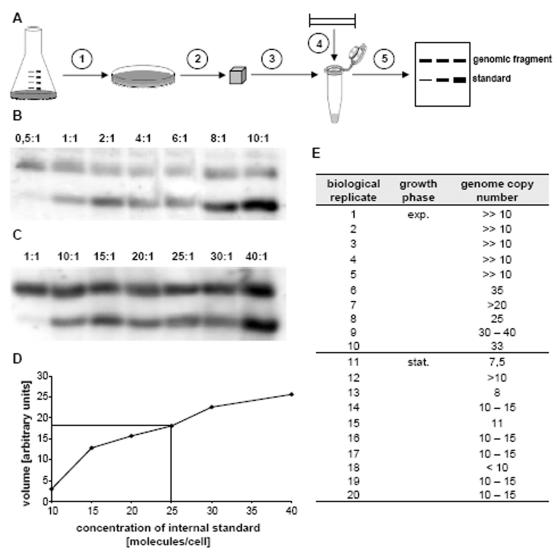
Figure 1.
A. Overview of the method. A culture of known cell density is embedded in low melting point agarose (step 1), agarose blocks with a defined number of cells are prepared, the cells are lysed and protein is digested (step 2). The blocks are melted and a restriction enzyme (step 3) as well as an internal standard (step 4) are added. After overnight digestion, DNA fragments are size fractionated by electrophoresis and a Southern blot is performed (step 5). A 1 kbp genomic fragment near the replication origin and the 0.9 kbp internal standard are both visualized with a single probe. Multiple aliquots containing different standard concentration are used for quantitation. B. Quantitation of the genome copy number of exponential cells. After gel electrophoresis and southern blotting, a genomic fragment (upper band) and different concentrations of an internal standard (lower band) were visualized with the same probe (step 5 in A). C. Quantitation of the genome copy number of stationary phase cells. After gel electrophoresis and Southern blotting, a genomic fragment (upper band) and different concentrations of an internal standard (lower band) were visualized with the same probe (step 5 in A). D. An example of a standard curve generated after quantitation of the bands shown in B. and C. The horizontal and vertical lines show the usage of the standard curve to determine the genome copy number in the biological replicate No. 9 (see E.). E. Summary of the results of the independent cultures that were used to determine the genome copy number with the “agarose block method”. In the first five experiments, the standard curve ranged from 0.5 molecules/cell to 10 molecules/cell (as in B.). The signal of exponential phase cells was much higher than the highest signal of the standard curve and could not be quantitated. Therefore the standard curve was chosen to range from 1 molecules/cell to 40 molecules/cell (as in C.) in subsequent experiments.