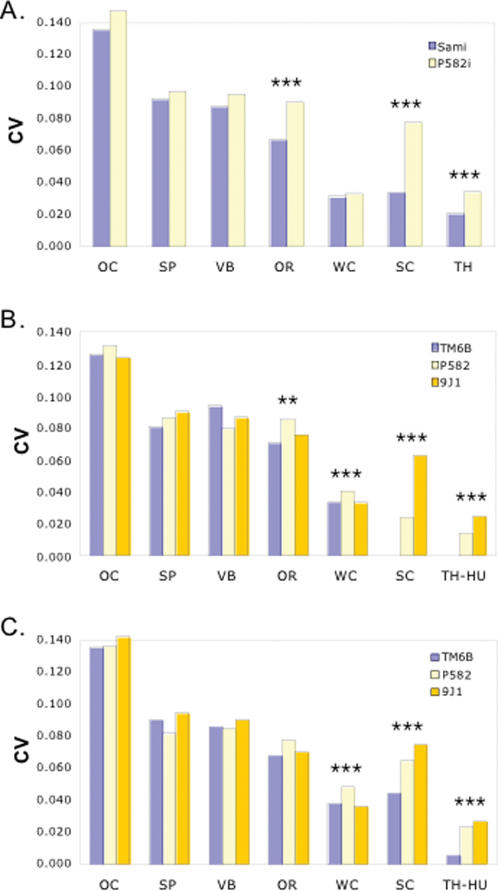
Figure 2. Hsp90 controlled phenotypic variation of most invariant quantitative traits.
(A) Effects of P582i (yellow) and Sami (blue) alleles of Hsp90 in the isogenic Sam background on VP of mutant and control sets of 450 males across the 9 RI line backgrounds.
(B and C) Effects of 3rd chromosomes carrying null (P582), and dominant-negative (9J1) Hsp90 mutations or wild-type Sam alleles introgressed into the Sam background in mutant and control sets of 225 male or 225 female sibs.
TM6B contains the dominant Humeral (Hu) mutation [32], which increases humeral TH bristle numbers.
Therefore, for comparison of TH bristles between TM6B and the other genotypes we used TH-HU, indicating that TH was scored only for the remaining 18 non-humeral TH bristle types.
All experiments were conducted under temperature, density and humidity controlled conditions.
Environmental effects were further controlled by direct comparisons between flies from the same vial and maternal environments.
Coefficients of variation (CV = standard deviation/mean) are shown to enable between-trait comparisons. Statistical tests of the significance of Hsp90 effects on phenotypic variability and P-values are found in Table 1 (for A) and Table 2 (for B and C).