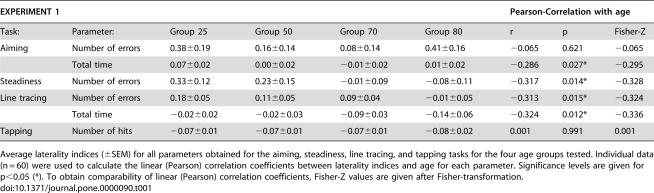
Table 1. Laterality indices of fine motor performance in different age groups.
| EXPERIMENT 1 | Pearson-Correlation with age | |||||||
| Task: | Parameter: | Group 25 | Group 50 | Group 70 | Group 80 | r | p | Fisher-Z |
| Aiming | Number of errors | 0.38±0.19 | 0.16±0.14 | 0.08±0.14 | 0.41±0.16 | −0.065 | 0.621 | −0.065 |
| Total time | 0.07±0.02 | 0.00±0.02 | −0.01±0.02 | 0.01±0.02 | −0.286 | 0.027* | −0.295 | |
| Steadiness | Number of errors | 0.33±0.12 | 0.23±0.15 | −0.01±0.09 | −0.08±0.11 | −0.317 | 0.014* | −0.328 |
| Line tracing | Number of errors | 0.18±0.05 | 0.11±0.05 | 0.09±0.04 | −0.01±0.05 | −0.313 | 0.015* | −0.324 |
| Total time | −0.02±0.02 | −0.02±0.03 | −0.09±0.03 | −0.14±0.06 | −0.324 | 0.012* | −0.336 | |
| Tapping | Number of hits | −0.07±0.01 | −0.07±0.01 | −0.07±0.01 | −0.08±0.02 | 0.001 | 0.991 | 0.001 |
Average laterality indices (±SEM) for all parameters obtained for the aiming, steadiness, line tracing, and tapping tasks for the four age groups tested. Individual data (n = 60) were used to calculate the linear (Pearson) correlation coefficients between laterality indices and age for each parameter. Significance levels are given for p<0.05 (*). To obtain comparability of linear (Pearson) correlation coefficients, Fisher-Z values are given after Fisher-transformation.