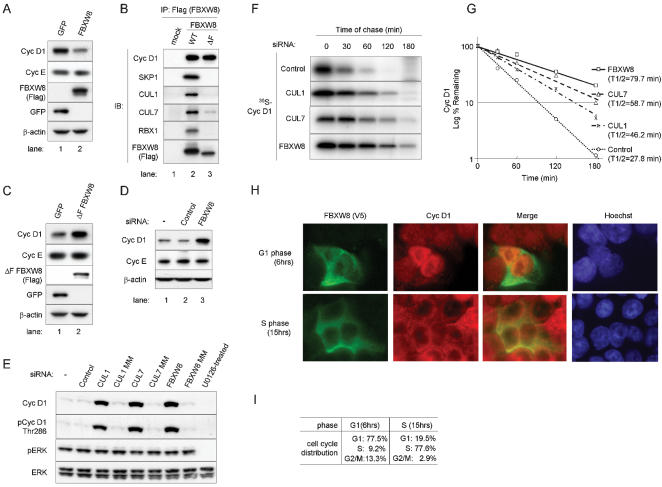
Figure 4.
The stability of cyclin D1 is regulated by FBXW8 complexes through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. (A, C) IB analysis. HCT 116 cells were infected with a retrovirus expressing FBXW8 (A), a ΔF mutant form (ΔF FBXW8, Panel C) or a control retrovirus expressing GFP (A, C). Forty-eight hours later, cells were harvested and Western blot analysis was performed with antibodies to cyclin D1, cyclin E, Flag (FBXW8 and ΔF FBXW8), GFP and β-actin. (B) IP–IB analysis. Empty (mock) or Flag-tagged WT FBXW8, and ΔF FBXW8 DNA plasmids were transiently transfected in T98G cells. Samples were precipitated with a Flag epitope tag antibody. Immunoprecipitates were subjected to SDS-PAGE and subsequently blotted with antibodies to cyclin D1, SKP1, CUL1, CUL7, RBX1 and Flag (F-box proteins). (D) IB analysis following depletion of FBXW8 expression for 48 hrs through siRNA in HCT 116 cells. Non-targeting siRNA (Control) and mock transfection (−) were controls. (E–G) Knockdown of FBXW8 or its partner CUL1 or CUL7 through siRNA stabilizes cyclin D1 expression in HCT 116 cells. (E) IB analysis following depletion of CUL1, CUL7 or FBXW8 expression for 48 hrs through siRNA or mismatch (MM) oligonucleotides in HCT 116 cells. Non-targeting siRNA (Control) and mock transfection (−) were controls. (F, G) Pulse-chase analysis of cyclin D1 following depletion of CUL1, CUL7 or FBXW8 expression for 48 hrs through siRNA in HCT 116 cells. Control cells were treated with non-targeting siRNA. Cells were pulse-labeled with 35S-methionine for an hour, chased with cold methionine as indicated, and then lysed. Cyclin D1 was immunoprecipitated and analyzed via SDS-PAGE. (G) Levels of metabolically labeled-cyclin D1 were estimated by quantitative scanning using Quantity One software and plotted graphically to determine the half-life of cyclin D1. (H, I) Immunofluorescence. Nuclei were visualized with Hoechst dye. Subcellular localization of E3 ligase. HCT 116 cells were transfected with V5 epitope-tagged FBXW8 pcDNA3. Cells were synchronized 24 hrs later by sequential manipulation of serum starvation and stimulation. At 6 hrs (G1 phase) or 15 hrs (S phase), cells were fixed. Immunofluorescence was performed with a V5 epitope tag antibody followed by Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated anti-mouse IgG antibody (green) and a rabbit cyclin D1 polyclonal antibody followed by Alexa Fluor 594-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (red). (I) Cell cycle distributions.