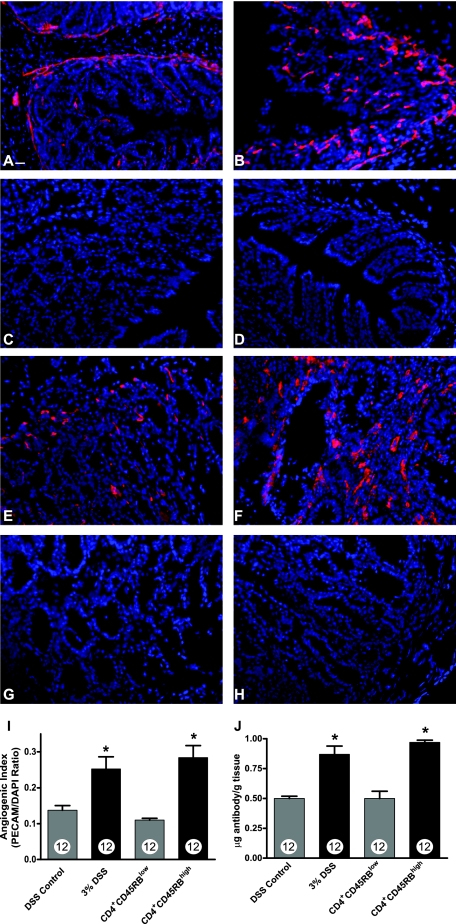
Figure 1.
PECAM-1 blood vessel density measurement during experimental colitis. Vascular density of normal and diseased colons was determined by staining frozen sections with anti-PECAM-1 antibody (red) followed by DAPI nuclear counterstaining (blue). A: PECAM-1 staining of normal DSS vehicle-treated colon tissue. B: Increased PECAM-1 staining of 3% DSS-treated colon tissue. C: Secondary antibody control staining of DSS-treated colon tissue. D: DAPI alone staining of DSS-treated colon tissue. E: PECAM-1 staining of CD4+CD45RBlow T-cell transfer control colon tissue. F: Enhanced PECAM-1 staining of CD4+CD45RBhigh T-cell transfer colitis tissue. G: Secondary antibody control staining of CD4+CD45RBhigh T-cell transfer colitis tissue. H: DAPI alone staining of CD4+CD45RBhigh T-cell transfer colitis tissue. I: Quantitative measurement of vascular density in the tissue sections as determined by calculating and angiogenic index that is derived from the total PECAM-1 surface area divided by the total DAPI surface area. J: The amount of radiolabeled PECAM-1 antibody binding within the colon vasculature demonstrating a significant increase in vessel surface area during experimental colitis. n values for each condition are reported within the bar graph. *P < 0.05 versus control. Original magnifications, ×200. Scale bar = 100 μm.