Abstract
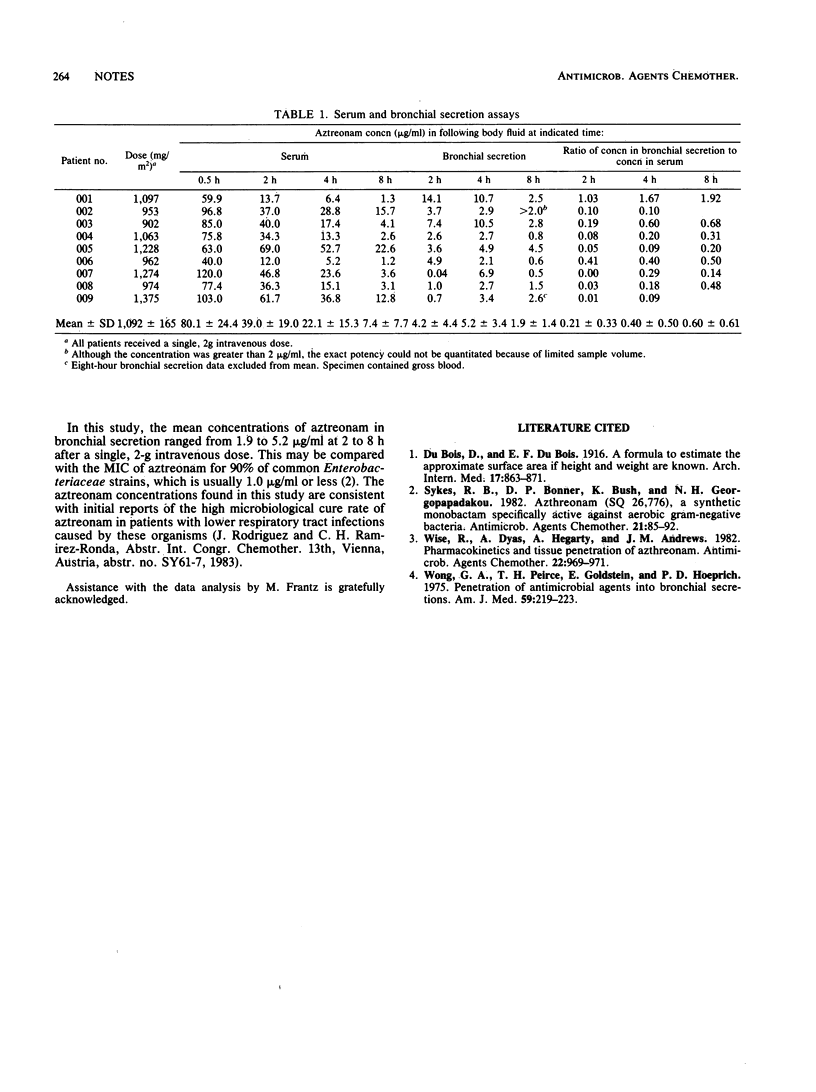
Nine intubated patients were given a single, 2-g intravenous dose of aztreonam over 5 min. Samples of serum and bronchial secretion were obtained 2, 4, and 8 h after administration and assayed for aztreonam content. The mean concentrations in bronchial secretion ranged from 1.9 to 5.2 micrograms/ml and tended to be highest at 4 h. The concentrations in bronchial secretion varied from patient to patient, but each patient had one or more bronchial secretion samples that contained at least 2.7 micrograms of drug per ml.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Sykes R. B., Bonner D. P., Bush K., Georgopapadakou N. H. Azthreonam (SQ 26,776), a synthetic monobactam specifically active against aerobic gram-negative bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jan;21(1):85–92. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Dyas A., Hegarty A., Andrews J. M. Pharmacokinetics and tissue penetration of azthreonam. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Dec;22(6):969–971. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.6.969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. A., Pierce T. H., Goldstein E., Hoeprich P. D. Penetration of antimicrobial agents into bronchial secretions. Am J Med. 1975 Aug;59(2):219–223. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90356-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


