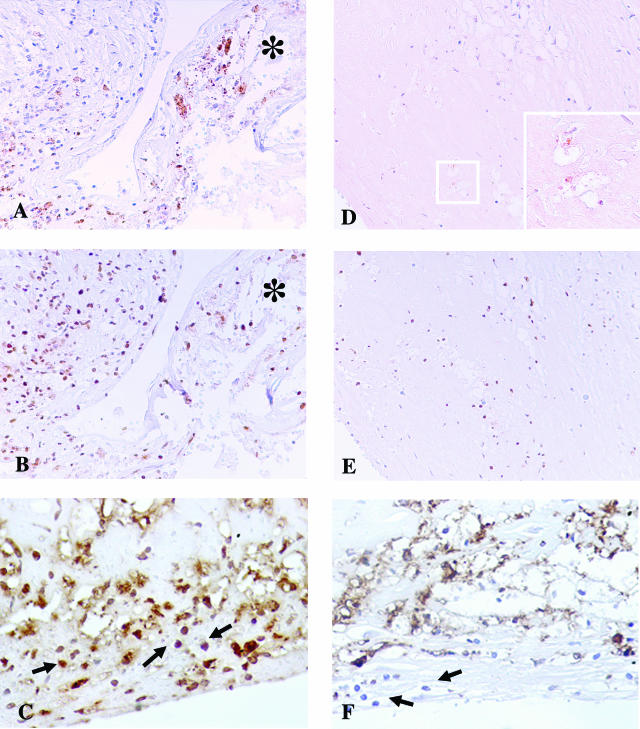
Figure 3.
Immunohistochemistry evidence of the presence of C. pneumoniae (CP) antigens within coronaries. A–C: Coronary artery of a patient who died of AMI. A strong immunoreactivity to OMP-2 antigens of CP (A) and to CP-HSP60 (B) was detectable in correspondence of the cap rupture. In AMI coronaries, immunohistochemical analysis showed also the presence of numerous inflammatory cells, constituted by macrophagic foam cells and T lymphocytes (arrow), positive for IFN-γ (C), indicating an activated state and a Th1-mediated immune response. *The flap of disrupted cap. D–F: Coronary artery of a patient without clinical cardiac history who died of noncardiac causes. D: A weak positive staining for OMP-2 antigens was detected only in few macrophagic cells. Inset: High-power magnification of the squared area. E: Weaker CP-HSP60 staining compared with AMI coronary plaques. The immunostaining to IFN-γ (F) was almost negative in the few infiltrating lymphocytes (arrow). Original magnifications: ×20 (A–E); ×60 (D, inset).