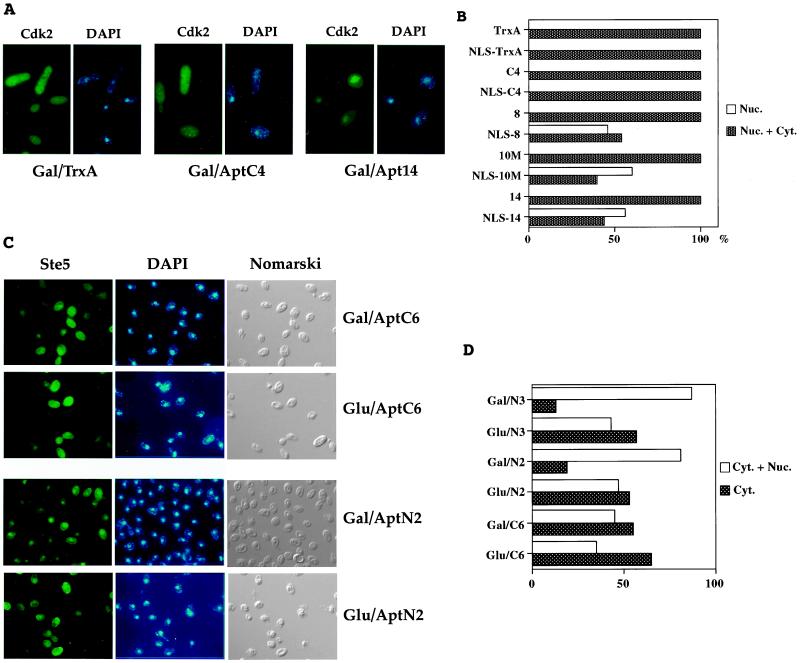
Figure 4.
Nuclear translocation of LexA-Cdk2 and LexA-Ste5 by interacting NLS-aptamer derivatives. (A) Yeast photomicrographs. (Left) Indirect immunofluorescence of LexA-Cdk2 protein using anti-LexA antibody. (Right) DNA staining with DAPI. Gal/TrxA, TrxA is expressed. Gal/AptC4, control aptamer C4 is expressed. Gal/Apt14, anti-Cdk2 aptamer 14 is expressed. (B) Percentage of yeast that displayed clear nuclear immunofluorescence, in presence of aptamers addressed to the nucleus or not. Dark bars, nuclear and cytoplasmic staining. White bars, nuclear staining. At least 50 cells were observed for each assay. (C) Yeast photomicrographs. (Left) Indirect immunofluorescence of LexA-Ste5 fusion protein using anti-LexA antibody. (Center) DNA staining with DAPI. (Right) Yeast observed with Nomarski optics. Gal/AptC6, non-NLS aptamer C6 is expressed. Glu/C6, non-NLS aptamer C6 is not expressed. Gal/AptN2, NLS-aptamer N2 is expressed. Glu/N1, NLS-aptamer N2 is not expressed. (D) Percentage of yeast that displayed cytoplasmic + nuclear or purely cytoplasmic staining, in presence of various aptamers addressed to the nucleus or not. Dark bars, cytoplasmic staining. White bars, cytoplasmic and nuclear staining. At least 100 cells were observed for each assay.