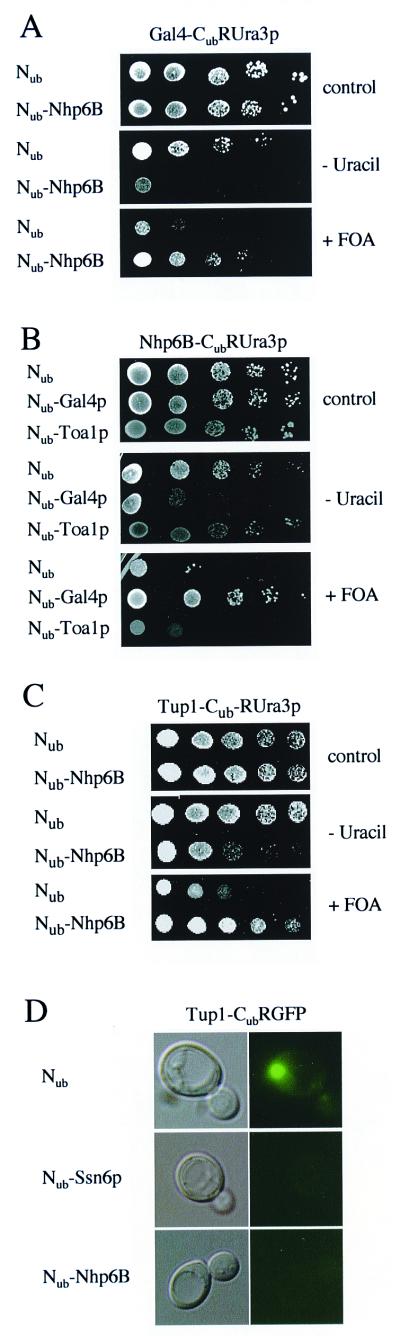
Figure 2.
Nhp6B was isolated in two independent split-ubiquitin screens using Gal4p or Tup1p as Cub-RUra3 baits. (A) Gal4p interacts with Nhp6B in vivo. Serial dilutions of cells coexpressing Nub or an Nub-Nhp6B fusion together with a fusion of the DNA-binding and activation domains of Gal4(1–147 + 768–881)p to Cub-RUra3p were grown on plates lacking tryptophan and leucine (Top), on plates additionally lacking uracil (Middle), or on plates containing FOA (Bottom). Nub and Nub fused to full-length Nhp6B were expressed from multicopy vectors. (B) The activation domain of Gal4p is sufficient for the interaction with Nhp6B. Serial dilutions of cells coexpressing Nub, Nub fused to the activation domain of Gal4p (amino acids 768–881; Nub-Gal4p), or Nub attached to the large subunit of TFIIA (Nub-Toa1p) together with Nhp6B-Cub-RUra3p were grown on plates lacking tryptophan and leucine (Top), on plates additionally lacking uracil (Middle), or on plates containing FOA (Bottom). Nub, Nub-Gal4p, and Nub-Toa1p were expressed from multicopy vectors. (C) Tup1p interacts with Nhp6B in vivo. Serial dilutions of cells coexpressing the depicted Nub and Cub fusions were grown on plates lacking tryptophan and leucine (Top), on plates additionally lacking uracil (Middle), or on plates containing FOA (Bottom). Nub and the clone isolated from the library expressing Nub-Nhp6B that lacked the first 22 amino acids of Nhp6B were on multicopy vectors. (D) Tup1-Cub-RGFP is located in the nucleus and interacts with Nub-Ssn6p and Nub-Nhp6B. Cells expressing the depicted fusions from single-copy vectors were analyzed under a Leitz fluorescence microscope with phase contrast (Left) and fluorescence (Right).