Figure 7.
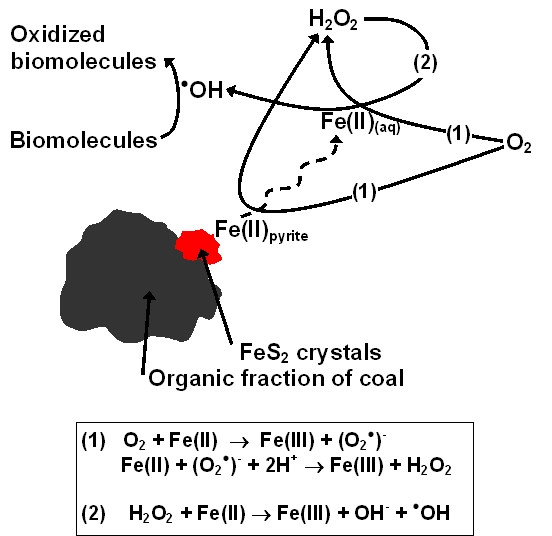
Mechanisms whereby coal that contains pyrite reacts with dissolved oxygen to generate H2O2 and •OH, with •OH leading to biomolecule degradation. In this diagram, dissolved oxygen reacts with either ferrous iron at the pyrite surface or dissolved Fe(II) to form H2O2 through the Haber-Weiss reactions (1), which may react with dissolved Fe(II) to form •OH through the Fenton reaction (2).
