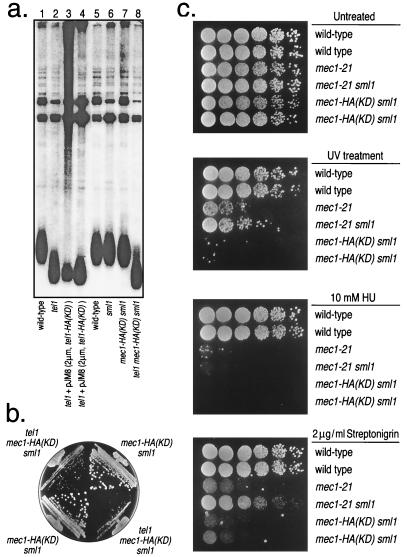
Figure 4.
Phenotypes of strains with mutations in the kinase domains of Tel1p and Mec1p. (a) Assay for telomere length. DNA was isolated from strains of various genotypes and treated with PstI. The resulting fragments were separated by gel electrophoresis and hybridized to a telomeric-specific probe as described in Materials and Methods. The dispersed band near the bottom of the gel represents the terminal-DNA fragments of chromosomes with Y′-containing telomeres. The strain name and genotype (indicated in parentheses) in each lane are: lanes 1 and 5, W303a (wild-type); lane 2, JMY303–2a (tel1); lanes 3 and 4, JMY103 [tel1 + plasmid-borne TEL1-HA(KD)]; lane 6, JMY73 (sml1); lane 7, JMY314–3d [mec1-HA(KD) sml1 rad5]; and lane 8, JMY313–9a [mec1-HA(KD) sml1 tel1∷ura3]. (b) Assay for growth. Spore colonies derived from the diploids JMY313 and JMY314 were streaked onto plates containing rich growth medium and incubated at 30o for 2 days. The two tel1 mec1-HA(KD) sml1 strains are JMY313–3a and JMY313–9a, and the two mec1-HA(KD) sml1 strains are JMY314–3d and JMY314–5a. (c) Assay of response to DNA-damaging agents. Serial dilutions of six strains were prepared on four plates containing rich growth medium (yeast extract/peptone/dextrose). One plate was untreated without any DNA-damaging agent; one was treated for 10 sec with UV light derived from a germicidal lamp; one contained 10 mM hydroxyurea (HU); and one contained 2 μg/ml streptonigrin. The strains used in the study (row 1 at the tops of the plates) were: row 1, W303a; row 2, W1588–4c (identical to W303a except RAD5 instead of rad5–535); row 3, JMY303–1c; row 4, JMY303–8d; row 5, JMY314–3d; and row 6, JMY314–5a (identical to JMY314–3d except RAD5). Cells were grown for 2 days at 30°C.