Fig. 7.
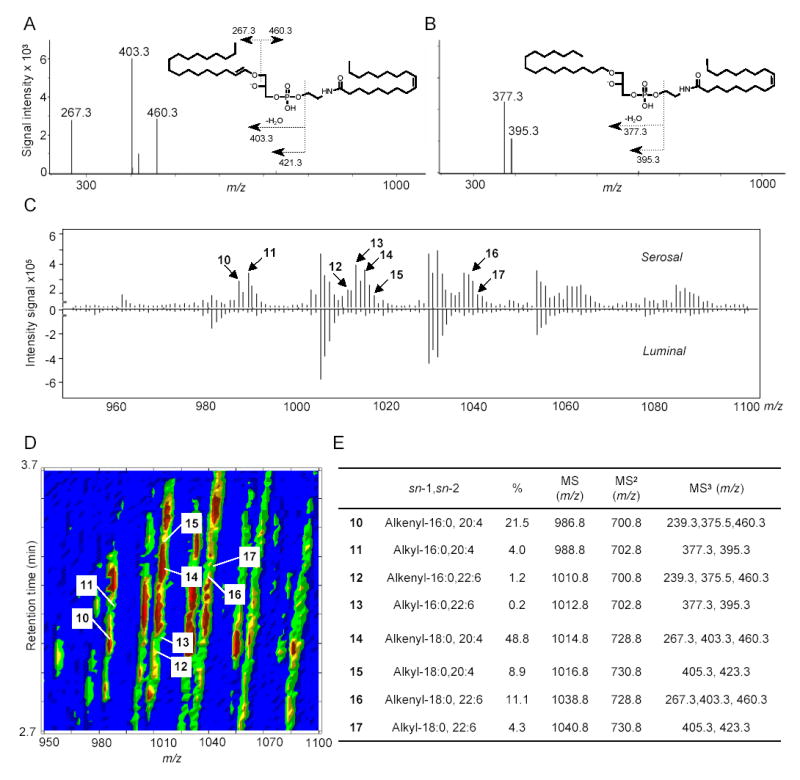
Molecular composition and relative quantification of OEA-generating NAPE species in the serosal layer of rat jejunum. MS3 fragmentation of representative sn-1 alkenyl NAPE (A) and sn-1 alkyl NAPE (B) identified in jejunal serosal layer. C, Mirrored display of averaged MS1 spectra at retention time from 2.7 to 3.7 min of serosal (top) and luminal (bottom) NAPEs. Arrows denote alkyl or alkenyl NAPE species. Numbers refer to the identification of those species, reported in panel E. D, Representative bidimensional LC/MS contour map of NAPEs from jejunal serosal fraction. The first dimension is elution time and the second is m/z. The colored density distribution represents relative intensity of the signal. Each number denotes an individual pseudo-molecular ion for 1-alkenyl (alkyl), sn-2-acyl NAPE species (10–17). E, ESI-MSn identification, sn-1 and sn-2 fatty acid composition and relative amounts (%) of the main OEA-generating ether-containing NAPEs in jejunal serosal fraction.
