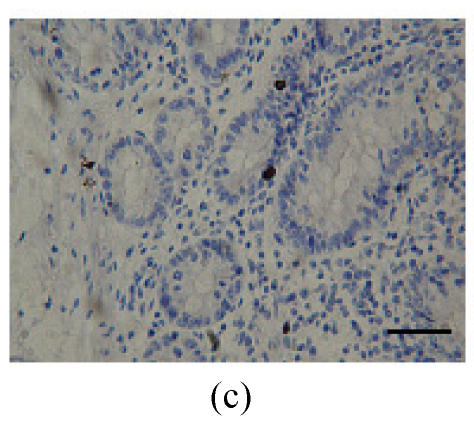
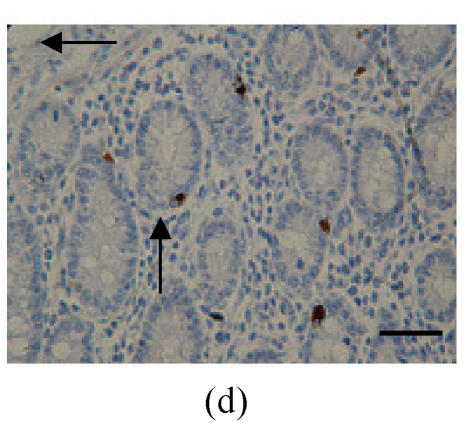
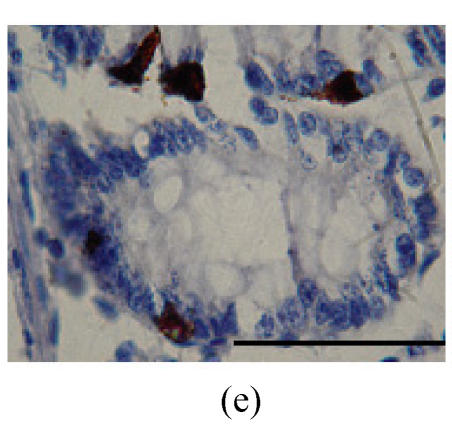
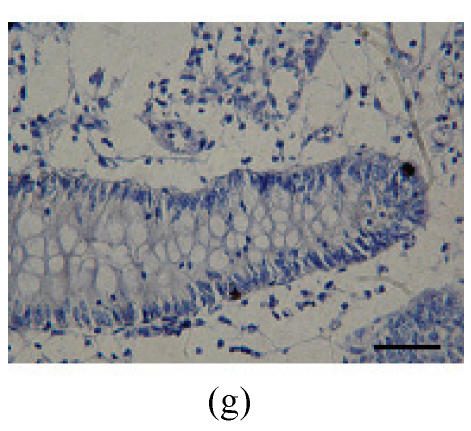
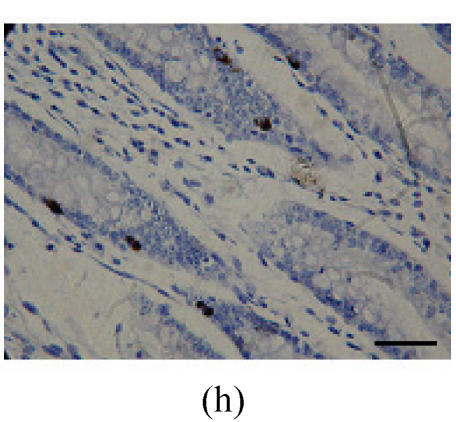
Fig. 2.
Immunohistochemical localization of FoxO proteins in the intestines of pigs (Bar=50 m). (a) Duodenum control (×400). →: Muscularis mucosa, ↓: Submucosa; (b) Localization of FoxO4 in the duodenum (×400). FoxO4 was obvious in the intestinal gland of duodenum. The localization was basically all at the base of the mucosa, close to the muscularis mucosa. These immunostained cells were almost all in absorptive cells, and some goblet cells of one part, and none in the lamina propria; (c) Localization of FoxO4 in the jejunum (×400). Some FoxO4 staining was observed in the mucosa intestinal gland; with these localizations all in absorptive cells, little in goblet cells, and little in the lamina propria; (d) Localization of FoxO4 in the ileum (×400). FoxO4 observed is exist in the intestinal gland nuclei may be absorptive cells and goblet cells. All of the localization is in the gland or near the gland, but not in the lamina propria. ←: Muscularis mucosa, ↑: Intestinal gland; (e) Localization of FoxO4 in the colon (×1000). FoxO4 was found mainly in the cell nuclei of the intestinal glands, and around the intestinal gland, with less localization in the lamina propria, and no expression in the submucosa and muscularis. Both absorptive cells and goblet cells possibly show FoxO4; (f) Localization of FoxO3a in the colon (×1000). FoxO3a staining was shown here in the cell nuclei of the lamina propria, but not in intestinal gland cells; and also in the muscularis of blood vessels viewed microscopically at 100 magnification; (g) Localization of FoxO4 in the cecum (×400). FoxO4 found here in nuclei of the intestinal gland was possibly absorptive cells and/or goblet cells; (h) Localization of FoxO4 in the rectum (×400). The localization of FoxO4 in nuclei of the intestinal gland of the mucosa is very obvious; the cells may be absorptive cells, goblet cells, and/or endocrine cells