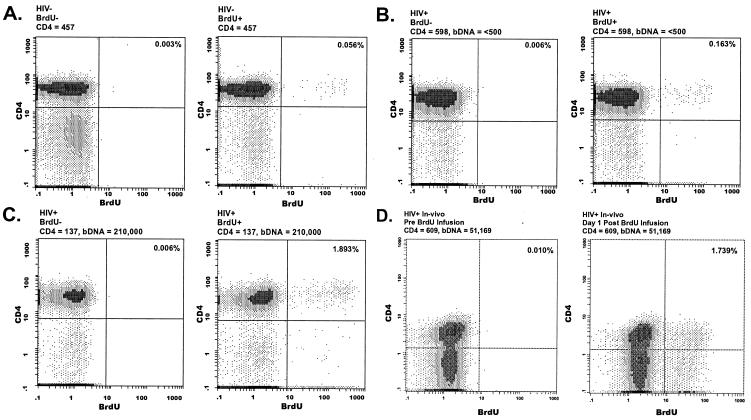
Figure 1.
Detection of BrdUrd-labeled CD4+ cells. EDTA anticoagulated whole blood samples were drawn from an uninfected individual (A) and two patients infected with HIV-1, one with low viral load and high CD4+ count (B) and one with high viral load, low CD4 count (C), and assayed for ex vivo BrdUrd incorporation into CD4+ T cells. (A–C) Whole blood was incubated with (Right) and without (Left) BrdUrd for 4 h at 37°C. (D) BrdUrd incorporation into CD4+ T cells of an individual with HIV-1 infection was determined before (Left) and 1 day after (Right) a 30-min infusion of BrdUrd (200 mg/m2). Cell surface staining and flow cytometric analysis of ex vivo- and in vivo-labeled cells were performed by using the same procedure.