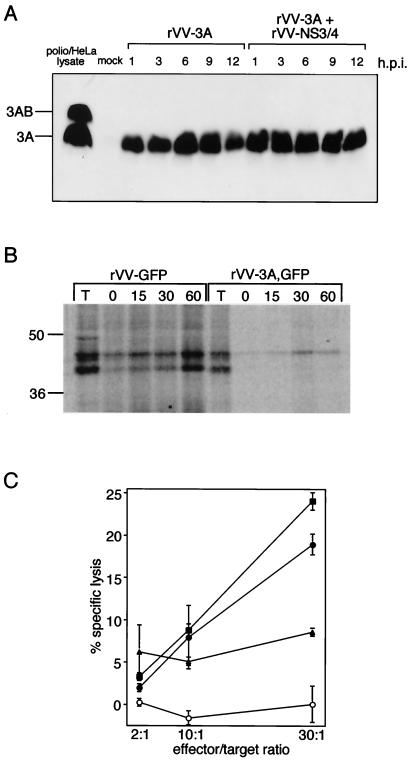
Figure 1.
(A) Expression of poliovirus 3A from rVV-3A,GFP. Immunoblot analysis of lysates from chimpanzee lymphocytes that were mock-infected, infected with rVV-3A/GFP, or coinfected with rVV-3A/GFP and rVV-E2/NS3. Time courses in hours after infection (h.p.i.) are shown. Lysate from poliovirus-infected HeLa cells shows both 3A and its precursor 3AB. (B) Effect of 3A protein on cell-surface expression of newly synthesized MHC class I. Chimpanzee B lymphoblastoid cells were infected with rVV-GFP or rVV-3A,GFP, labeled with [35S]methionine and [35S]cysteine for 15 min, and subsequently incubated with nonradioactive amino acids for various periods of time. Molecules on the cell surface were subjected to biotinylation and recovered by use of streptavidin agarose. Total (T) MHC class I molecules after 60 min of chase and MHC class I molecules that appeared at the cell surface after the indicated times (min) were isolated by immunoprecipitation with anti-MHC class I antibody w6/32. Molecular masses (kDa) of marker proteins are indicated. (C) Effect of poliovirus 3A on target-cell lysis by CTL. Chimpanzee B lymphoblastoid target cells were infected with wild-type vaccinia (○), infected with rVV-E2/NS3 alone (■), or coinfected with rVV-E2/NS3 and rVV-GFP (●) or rVV-E2/NS3 and rVV-3A,GFP (▴). At 12 h postinfection, target cells were labeled with 51Cr and incubated for 4 h with T91 CTL at the indicated effector/target ratios. Specific lysis was expressed as the amount of 51Cr released into the supernatant as a percentage of the total counts per sample. Data are presented as the mean of triplicate samples, and the standard deviations are indicated.