Fig. 2.
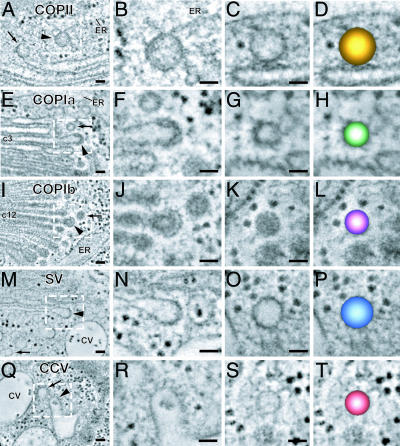
A gallery of tomogram slice images displaying examples of the five vesicle types associated with the transitional ER (A–D), cis cisternae (E–H), medial or trans cisternae (I–L), trans-most cisterna (M–P), and contractile vacuole (Q–T) of S. dubia. The budding profiles of the five types of vesicles display distinct coat morphologies (magnified in the second column). The COPII-type coat appears thin and is relatively tight against the ER membrane (B). The COPIa-type coat appears thicker and more diffuse (F), whereas the COPIb-type coat appears spaced out away from the cisternal membrane (J). The coats on the budding vesicles on the trans-most cisterna resemble COPII (N), and the clathrin coats on the CV system (R) have a characteristic clathrin structure and spacing. For each type of budding profile, vesicles with identical diameters and staining patterns are found nearby (arrows). Color-coded models of each type of vesicle are shown in the fourth column (D, H, L, P, and T). (Scale bars, 50 nm.)