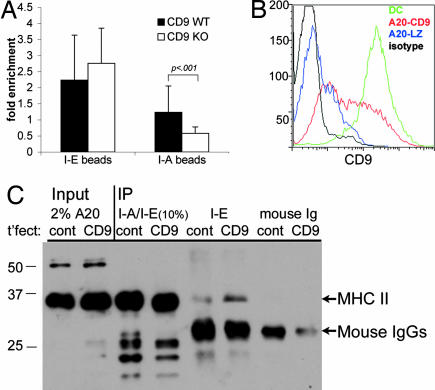
Fig. 6.
CD9 is necessary for I-A/I-E clustering. (A) DCs raised from the BM of CD9 WT vs. knockout mice and retrovirally transduced with I-Eα-GFP were adhered to coverslips and allowed to interact with I-E- or I-A-coated beads as in Fig. 2. Fluorescence at sites of bead adherence was quantified as described in Fig. 3. (B) A20 B lymphoma cells were transfected with CD9 cDNA (red line) or lacZ as a control (blue line). DCs are shown for comparison (green line). Black line, isotype control. (C) CHAPS lysates (1%) of stable cells lines (A20 cells transfected with CD9, lane 6, or a control plasmid, cont., lane 5) were immunoprecipitated with Ab to I-A or I-E as in Fig. 4, and I-A was visualized by Western blotting. Total MHC II was precipitated with TIB120, specific for both I-A and I-E in these cells (lanes 3 and 4). IP with an irrelevant Ab is shown in lanes 7 and 8. Arrows indicate MHC II and mouse IgG bands.