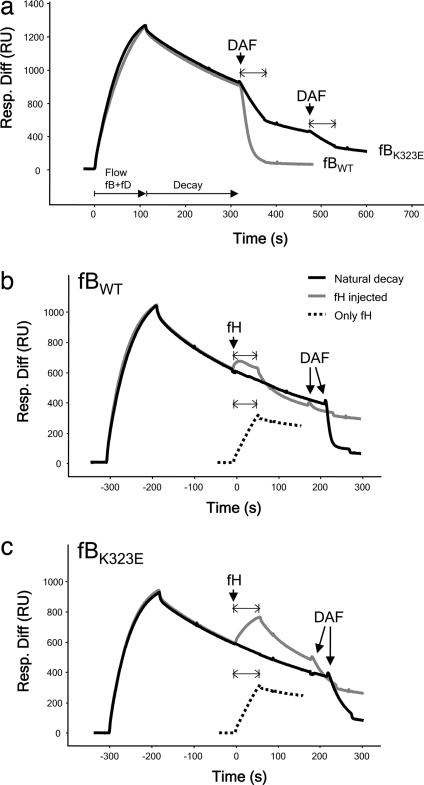
Fig. 5.
fBK323E convertase decay by sDAF or fH monitored by SPR. (a) Decay by sDAF. C3bBb was allowed to decay spontaneously for several minutes before injection of sDAF. Bb from fBWT was removed from the surface by accelerated decay, whereas Bb formed from fBK323E demonstrated a much slower rate of accelerated decay. (b) Decay of fBWT by fH. After a period of spontaneous decay, fH or buffer (“natural decay”) was injected over the surface. Mass of protein bound reflected a balance between fH binding to C3b and Bb release. To visualize the binding of fH to C3b in isolation, fH was injected over the C3b surface (“only fH”). To confirm efficiency of fH decay, DAF was flowed and released no more Bb. (c) Decay of fBK323E by fH. Injects were as described above. Bb from fBK323E was much less efficiently decayed by fH as evidenced by the increased protein mass at the surface during the inject and the presence of residual Bb revealed by DAF-mediated decay. Resp. Diff, response difference; RU, resonance units.