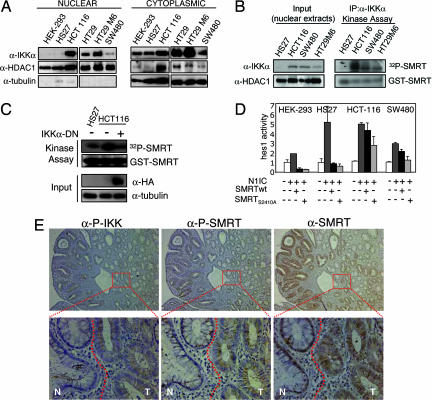
Fig. 2.
Nuclear IKKα phosphorylates SMRT and associates with its cytoplasmic translocation in colorectal tumors. (A) Western blot analysis of IKKα in cytoplasmic and nuclear extracts from the different cell lines. α-HDAC1 and α-tubulin are used as fractionation and loading controls. (B) Kinase activity assay of precipitated nuclear IKKα tested on GST-SMRT (amino acids 2321–2525) detected by [32P]ATP incorporation. Nuclear levels of IKKα in the different cell lines and HDAC1 as a nuclear input control are shown. (C) Kinase activity assay of total extracts from cells transfected with or without DN-IKKα tested on GST-SMRT (amino acids 2321–2525) detected by [32P]ATP incorporation. Levels of transfected DN-IKKα are detected with α-HA antibody, and α-tubulin is used as a loading control. (D) Indicated cell lines were cotransfected with hes1-luc and the indicated constructs. The graph represents the activity of hes1-luc in the different conditions. The average and standard deviation from duplicates of one representative of three experiments are shown. (E) IHC of sequential sections containing both normal (N) and adenoma (T) tissue (see dotted line) with α-P-IKKα/β, α-P-SMRT, and α-SMRT antibodies. Images were obtained at ×100 and ×600.