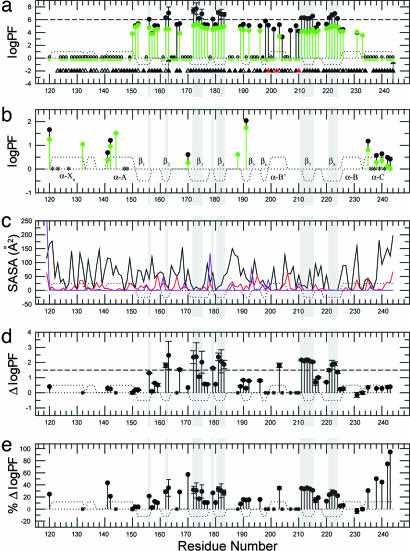
Fig. 2.
PFs of RIα (residues 119–244) based on H/D and H/H exchange. (a) PFs derived from H/D exchange rates measured for RIα (residues 119–244) with (black) and without (green) 10-fold excess cAMP at 306 K and in 50 mM Mes (pH 6.5)/100 mM NaCl/0.02% NaN3. Filled circles indicate amide protons that exchange slowly enough to enable the measurement of quantitative H/D exchange rates; empty circles denote amide protons that were fully exchanged within the dead time of the experiment (≈20 min); stars indicate amide protons that could be detected only in the first HSQC spectrum acquired after exposure to D2O, but not in the subsequent spectra. The triangles indicate the presence of hydrogen bonds donated by the backbone amide hydrogen. Filled triangles indicate hydrogen bonds with H O distance <2.40 Å and H-N … O angle <35°, and open triangles indicate hydrogen bonds fulfilling less severe geometric criteria (H
O distance <2.40 Å and H-N … O angle <35°, and open triangles indicate hydrogen bonds fulfilling less severe geometric criteria (H O distance <2.85 Å and H-N … O angle <47°). Red triangles represent intermolecular (protein-cAMP) hydrogen bonds. The arrow at I163 signifies that for this residue no significant HSQC intensity change was observed during the course of the H/D experiment and therefore the reported PF value should just be interpreted as a PF lower limit. The arrow at Y244 means that for this residue a bimodal behavior is observed in the presence of 10-fold excess cAMP: whereas most of the Y244 HSQC cross-peak intensity is lost in the first HSQC spectrum, a small but detectable residual signal remains until the completion of the H/D experiment. Residues for which no symbol is reported are ambiguous because of overlap or are prolines (P153 and P208). (b) PFs derived from H/H exchange rates measured under the same conditions reported for a. The green/black color coding is the same as in a. Residues 132, 144, and 188 exchange fast enough to result in detectable H/H exchange CLEANEX cross-peaks only in the absence of cAMP excess (green). Residues marked with a star could not be unambiguously assigned in the CLEANEX spectrum because of overlap. (c) Residue-specific SASAs for the bound form. The black solid line indicates the total (backbone and side-chain) SASAs, and the red line refers to the backbone-only SASAs. The violet line refers to SASAs for backbone N atoms scaled up by a factor of 10. The reported SASA values should be considered as upper limits because the shielding effect of tightly bound water molecules and cAMP is not accounted for. (d) Differences between the PF logarithms measured with and without cAMP excess, shown in a and b in black and green, respectively. (e) As in d, but showing the effect of cAMP excess removal as percentage variations in PF logarithms (i.e., 100 × ΔlogPF/logPFbound). In all images, dotted lines represent the secondary structure expected for RIα (residues 119–244) based on the coordinates of the cAMP-bound R-subunit (6). Positive dots indicate α-helices or turns, and negative dots denote β-strands. Gray shading indicates residues with log10(PF) > 6 in the cAMP bound form, i.e., class c residues. In d and e stars denote residues that exchange too fast in the absence of excess cAMP for a quantitative PF determination by H/D exchange or too slow in the presence of bound cAMP for the detection of H/H exchange cross-peaks.
O distance <2.85 Å and H-N … O angle <47°). Red triangles represent intermolecular (protein-cAMP) hydrogen bonds. The arrow at I163 signifies that for this residue no significant HSQC intensity change was observed during the course of the H/D experiment and therefore the reported PF value should just be interpreted as a PF lower limit. The arrow at Y244 means that for this residue a bimodal behavior is observed in the presence of 10-fold excess cAMP: whereas most of the Y244 HSQC cross-peak intensity is lost in the first HSQC spectrum, a small but detectable residual signal remains until the completion of the H/D experiment. Residues for which no symbol is reported are ambiguous because of overlap or are prolines (P153 and P208). (b) PFs derived from H/H exchange rates measured under the same conditions reported for a. The green/black color coding is the same as in a. Residues 132, 144, and 188 exchange fast enough to result in detectable H/H exchange CLEANEX cross-peaks only in the absence of cAMP excess (green). Residues marked with a star could not be unambiguously assigned in the CLEANEX spectrum because of overlap. (c) Residue-specific SASAs for the bound form. The black solid line indicates the total (backbone and side-chain) SASAs, and the red line refers to the backbone-only SASAs. The violet line refers to SASAs for backbone N atoms scaled up by a factor of 10. The reported SASA values should be considered as upper limits because the shielding effect of tightly bound water molecules and cAMP is not accounted for. (d) Differences between the PF logarithms measured with and without cAMP excess, shown in a and b in black and green, respectively. (e) As in d, but showing the effect of cAMP excess removal as percentage variations in PF logarithms (i.e., 100 × ΔlogPF/logPFbound). In all images, dotted lines represent the secondary structure expected for RIα (residues 119–244) based on the coordinates of the cAMP-bound R-subunit (6). Positive dots indicate α-helices or turns, and negative dots denote β-strands. Gray shading indicates residues with log10(PF) > 6 in the cAMP bound form, i.e., class c residues. In d and e stars denote residues that exchange too fast in the absence of excess cAMP for a quantitative PF determination by H/D exchange or too slow in the presence of bound cAMP for the detection of H/H exchange cross-peaks.