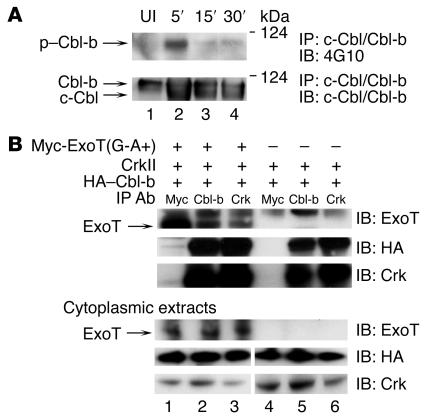
Figure 2. ExoT, Crk, and Cbl-b exist in a complex, and P. aeruginosa induces phosphorylation of Cbl-b.
(A) HeLa cells were coincubated with PA103ΔexoU/exoT(G-A+) for 5, 15, or 30 minutes. Cytoplasmic extracts were immunoprecipitated with anti–c-Cbl/Cbl-b Abs, H-454. Upper panel: lysates were immunoblotted with 4G10 to detect tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins. P. aeruginosa induced tyrosine phosphorylation of the upper band, Cbl-b, but not the lower band, c-Cbl. Lower panel: lysates were immunoblotted with anti–c-Cbl/Cbl-b Abs to detect total Cbl proteins. UI, uninfected. (B) HeLa cells were cotransfected with the indicated plasmids [Myc-ExoT(G-A+) and/or CrkII and HA–Cbl-b] for 18 hours and further incubated for 4 hours with 10 μM lactacystin. Cytoplasmic extracts were prepared, and proteins were immunoprecipitated with anti-Myc, anti–Cbl-b, or anti-Crk Abs. Coimmunoprecipitated ExoT was visualized by immunoblot using anti-ExoT Abs (upper panel). ExoT was coimmunoprecipitated with Cbl-b (lane 2) or CrkII (lane 3). Upper band visible in all the immunoprecipitations represents nonspecific binding to the ExoT Abs. Coimmunoprecipitated Cbl-b and Crk were visualized using anti-HA and anti-Crk Abs (bottom 2 panels). To measure expression of the transfected proteins, the cytoplasmic extracts were immunoblotted using anti-Myc, anti-HA, or anti-Crk Abs (lower 3 panels).