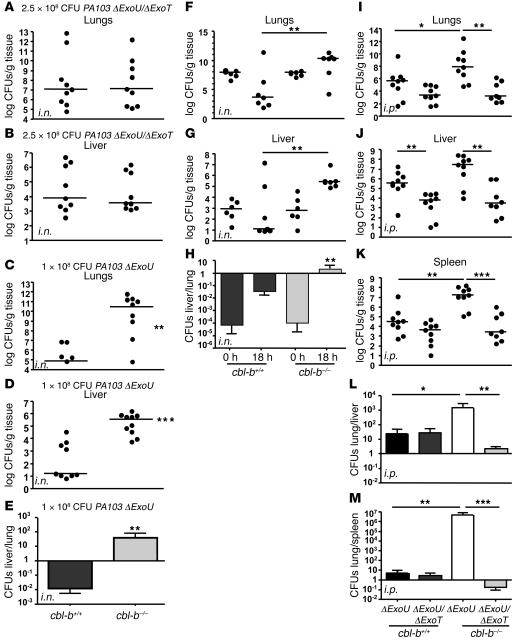
Figure 5. Cbl-b limits P. aeruginosa infection in an ExoT-dependent manner.
(A–E) C57BL/6 (cbl-b+/+) or C57BL/6 (cbl-b–/–) were infected i.n. with 2.5 × 108 of PA103ΔexoUΔexoT (A and B) or 1 × 108 of PA103ΔexoU (C and D). A higher dose of PA103ΔexoUΔexoT compared with PA103ΔexoU was necessary in order to quantify lung or liver CFUs at 18 hours. At 18 hpi, mice were sacrificed and bacterial CFUs were enumerated from the lung (A and C) and liver (B and D) tissues by plating serial dilutions of tissue homogenates on LB agar plates. (E) The average ± SEM of the liver/lung ratio of bacterial counts in cbl-b+/+ and cbl-b–/–mice was determined for each mouse. (F–G) cbl-b+/+ or cbl-b–/– mice were infected i.n. with 1 × 108 CFUs of PA103ΔexoU. Mice were sacrificed at the indicated times after infection, and bacterial CFUs in the lungs (F) and liver (G) were enumerated. Liver/lung ratio of bacterial counts was determined for each mouse and plotted as an average for cbl-b+/+ and cbl-b–/– mice (H). (I–M) cbl-b+/+ or cbl-b–/– were infected i.p. with 1 × 107 of PA103ΔexoUΔexoT or PA103ΔexoU. At 18 hpi, mice were sacrificed and bacterial CFUs were enumerated from the lungs (I), liver (J), and spleen (K). The lung/liver (L) or lung/spleen (M) ratio of bacterial counts was determined for each mouse and plotted as an average ± SEM for cbl-b+/+ and cbl-b–/–mice. Statistical analyses were performed by the 2-tailed Mann-Whitney U test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.005; ***P < 0.001.