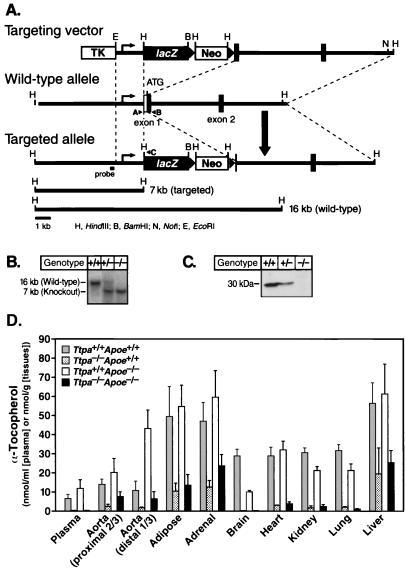
Figure 1.
Generation of Ttpa−/− mice. (A) Strategy for disrupting the Ttpa gene. On homologous recombination of the targeting vector with the Ttpa locus, lacZ (β-galactosidase) and neo genes are inserted into the 5′ untranslated sequences of exon 1, resulting in the deletion of the Ttpa translational start codon. A, B, and C represent primers used for PCR genotyping. (B) Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA from offspring of heterozygous intercrosses. (C) Absence of α-TTP protein in liver homogenates of Ttpa−/− mice. α-TTP protein levels were reduced by ≈50% in Ttpa+/− mice. (D) α-Tocopherol levels in Ttpa+/+Apoe+/+ and Ttpa−/−Apoe+/+ mice and in Ttpa+/+Apoe−/− and Ttpa−/−Apoe−/− mice, of 7–12 months of age. Aortic γ-tocopherol levels were similarly low in both Ttpa+/+Apoe−/− and Ttpa−/−Apoe−/− mice (0.60 ± 0.64 vs. 0.77 ± 0.68 nmol/g, P = 0.55). Data are expressed as mean ± SD.