Fig. 3.
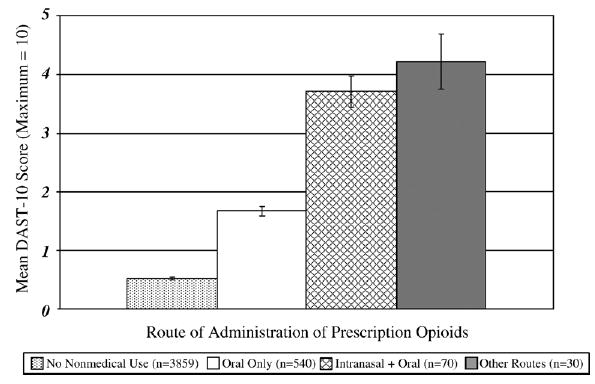
Mean DAST-10 scores as a function of route of administration of nonmedical prescription opioids. Error bars represent ± 1 S.E. Intranasal+oral (n=70) excluded other non-oral routes. Other routes (n=30) included smoking, injecting, and/or inhaling but did not exclude oral or intranasal. ANOVA showed a main effect of route of administration, F(3, 4473)=355.8, p<0.001. Post-hoc tests indicated the mean DAST-10 score among individuals who reported intranasal and other routes of administration was significantly higher than mean DAST-10 scores of non-users and nonmedical users who reported oral only route of administration (p<0.05).
